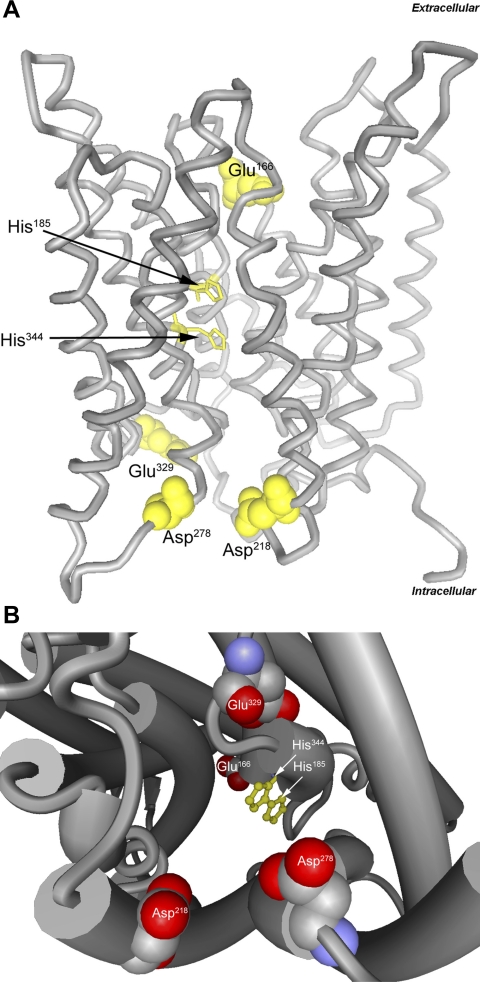
Fig. 8.
Molecular structure of human RhCG showing key residues. A: ribbon structure model with lateral view. Twin, coplanar histidine residues, His185 and His344, function to stabilize NH3 transport and provide selectivity relative to other solutes, such as NH4, and are shown in ball-and-stick representation. Acidic residues in extracellular and intracellular vestibules, function in NH4+ attraction and stabilization (Glu166, Asp218, Asp278, and Glu329), and are shown in space-filling representation. B: cytoplasmic view of channel, demonstrating key NH4+-stabilizing acidic residues (Asp218, Asp278, and Glu329), coplanar histidine residues in pore channel, and representation of extracellular vestibule acidic residue (Glu166). Models were generated using BallView software, version 1.3.2 using human RhCG data (3HD6).