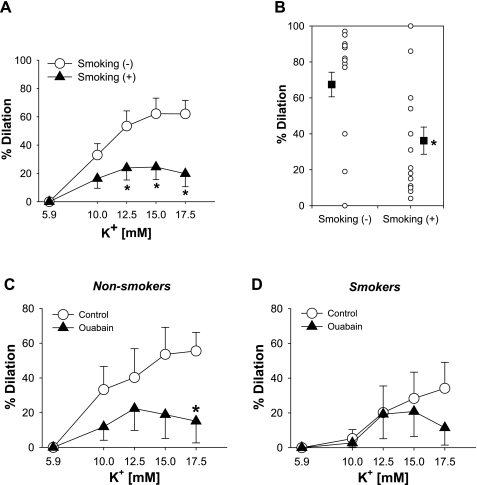
Fig. 3.
Influence of cigarette smoking on K+-induced vasodilation. A: the presence of tobacco use was associated with reduced vasodilation to K+ (n = 33). B: maximal dilations to K+ were also decreased in subjects who smoke cigarette (n = 18 nonsmokers and 15 smokers). C and D: the inhibitory effect of ouabain on vasodilation to K+ was substantial in HCAs from subjects without tobacco use (n = 7; C), whereas no inhibition was seen in those from subjects who smoke cigarette (n = 6; D). Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 vs. smoking(−) or control.