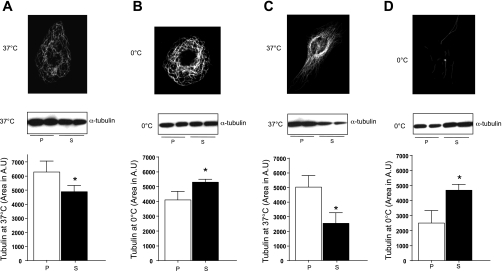
Fig. 3.
Microtubules and α-tubulin in microvascular endothelium vs. HeLa cells. A: at 37°C, pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVEC) have more polymerized than soluble tubulin. Top: immunofluorescence to detect α-tubulin in PMVEC cells at 37°C. Picture is representative of 6 independent experiments. Middle: immunoblot to detect polymerized (P) vs. soluble (S) α-tubulin following microtubule extraction at 37°C. Bottom: quantitation of immunoblot results. Data are representative of 5 independent experiments. B: following cold exposure, PMVEC have more soluble than polymerized tubulin; however, the change is not as dramatic as in HeLa cells. Top: immunofluorescence to detect α-tubulin in PMVEC at 0°C. Picture is representative of 6 independent experiments. Middle: immunoblot to detect polymerized vs. soluble α-tubulin following microtubule extraction. Bottom: quantitation of immunoblot results. Data are representative of 5 independent experiments. C: at 37°C, HeLa cells have more polymerized than soluble tubulin. Top: immunofluorescence to detect α-tubulin in HeLa cells at 37°C. Picture is representative of 6 independent experiments. Middle: immunoblot to detect polymerized vs. soluble α-tubulin following microtubule extraction. Bottom: data are representative of 5 independent experiments. D: following cold exposure, HeLa cells have more soluble than polymerized tubulin. Top: immunofluorescence to detect α-tubulin in HeLa cells at 0°C. Picture is representative of 8 independent experiments. Middle: immunoblot to detect polymerized vs. depolymerized α-tubulin following microtubule extraction. Bottom: quantitation of immunoblot results. Bottom values are means ± SD. Data are representative of 5 independent experiments. *P < 0.05. Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney test.