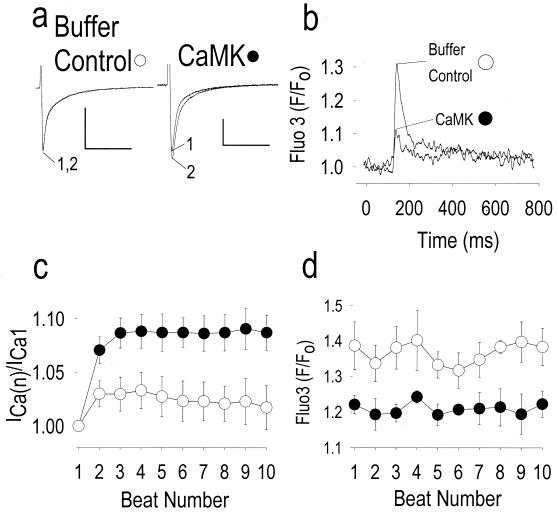
Figure 2.
Addition of constitutively active CaMK reconstitutes ICa facilitation and reciprocally reduces release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. (a) ICa facilitation is absent in this cell dialyzed with buffer solution (Buffer Control), but is present after addition of constitutively active CaMK (CaMK). Numerals indicate the beat number as in Fig. 1, and the calibration bars represent 500 pA (vertical) and 100 ms (horizontal). (b) Averaged intracellular Ca2+ transients using the fluorescent indicator fluo 3 (see Methods), for beats 1–10 to show the sustained reduction in Ca2+ release from intracellular stores by CaMK (n = 5) compared with buffer alone (n = 5). (c) Summary of data showing ICa facilitation expressed as the ratio of peak ICa during the first to the nth beat [ICa(n)], as shown in Fig. 1. ICa facilitation was significantly increased by CaMK (n = 5) compared with control (P < 0.05 for beats 2 and 4–10, n = 5). (d) Peak fluo 3 fluorescence signals for each stimulated beat, measured simultaneously with ICa reported in c. CaMK significantly reduced peak fluo 3 fluorescence compared with control (P < 0.05 for beats 3, 5, 8–10).