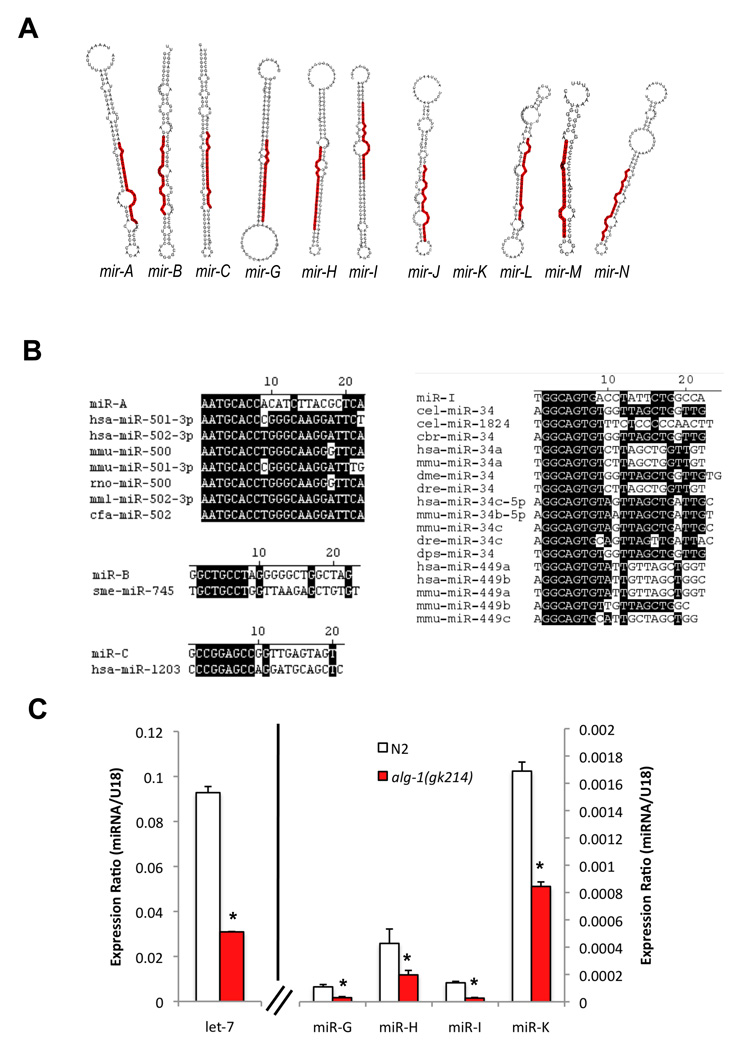
Figure 1. Novel miRNAs identified in aged C. elegans.
(A) Secondary structures of putative precursor hairpins corresponding to miRNAs identified in a pool of RNA enriched for aged C. elegans. The predicted mature sequence is highlighted in red.
(B) Conservation of novel miRNAs miR-A, miR-B, miR-C and miR-I to known miRNAs. Identical nucleotides are highlighted in black.
C) Validation of expression of candidate novel miRNAs. The expression of novel miRNAs mir-G, mir-H, mir-I and mir-K was confirmed by TaqMan qRT-PCR in wild-type (N2) C. elegans. Consistent with their classification as miRNAs, their expression was significantly reduced in alg-1(gk214) mutant animals. The expression of the miRNA let-7 is shown as a positive control. The expression of a non-miRNA small RNA species (snoRNA sn2429) does not change in alg-1(gk214) background (DNS). *, p < 0.05, alg-1(gk215) compared to wild-type (N2) (Student's t-test).