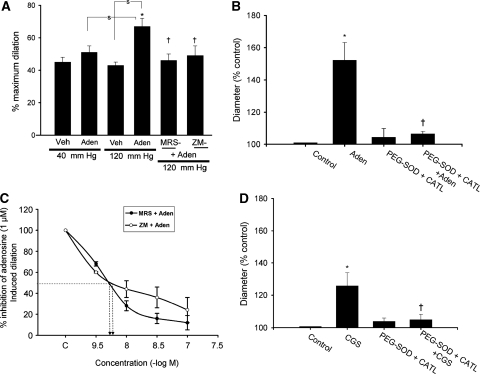
Figure 3.
Adenosine receptor subtypes and oxidants mediate adenosine-induced increase in diameter of pressure constricted cerebral arterial segments. (A) Role of adenosine receptor subtypes and oxidants in adenosine-induced increase in diameter of pressure constricted cerebral arterial segments. Bar graphs depicting the effects of exogenously applied adenosine (1 μmol/L) or vehicle on the diameter of cerebral arterial segments pressurized at 40 or 120 mm Hg before and after treatment with the A2B adenosine receptor antagonist MRS-1754 (20 nmol/L) or with the mixed A2A and A2B adenosine receptor antagonist ZM-241385 (100 nmol/L). Adenosine caused an increase in the diameter of the cerebral arterial segments pressurized at either 40 or 120 mm Hg that was significantly attenuated by the A2B adenosine receptor antagonist MRS-1754 and by the mixed A2A and A2B adenosine receptor antagonist ZM-241385. *Denotes the significant increase (P<0.05), and † represents the significant attenuation (P<0.05) of the adenosine-induced increase in the diameter of the arterial segments pressurized at 120 mm Hg by pretreatment with either MRS-1754 or ZM-241385 (n=6 for all groups studied). (C) Concentration-dependent inhibition of the adenosine (1 μmol/L)-induced increase in the diameter of pressurized cerebral arterial segments by the A2A adenosine receptor antagonist ZM-241385 (○) and by the A2B adenosine receptor antagonist MRS-1754 (•). (B and D) Effects of the antioxidants superoxide dismutase (SOD) conjugated to polyethylene glycol (PEG-SOD) and PEG-catalase on adenosine and CGS-21680 induced an increase in the diameter of pressure-constricted rat cerebral arterial segments. Preincubation of cannulated and pressurized cerebral arterial segments with a mixture of PEG-SOD (100 Units/mL) and PEG-catalase (100 Units/mL) had no significant effect on the control diameter, but significantly attenuated the increase in the diameter induced (panel B) by adenosine (1 μmol/L) and (panel C) by CGS-21680 (10 μmol/L). *Denotes the significant difference from control (P<0.05), and †denotes the significant difference from the increase in diameter induced by adenosine (panel A) or by CGS-21680 (panel B) (n=5 for each group).