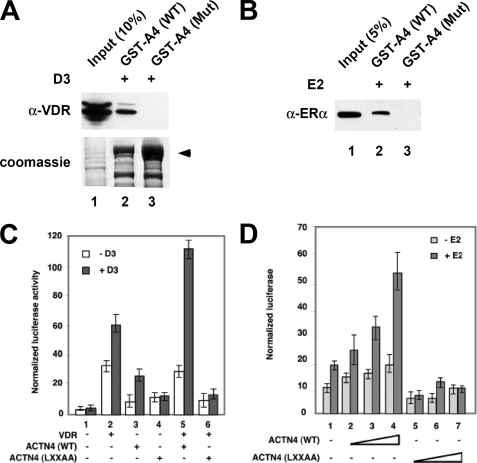
FIGURE 4.
LXXLL motif is essential for the ACTN4 to potentiate nuclear receptor-mediated transcriptional activity. A, ACTN4 (LXXAA) mutant loses its ability to interact with VDR. HEK293 cells were transfected with a VDR expression plasmid. 48-h post-transfection, the lysates were prepared and incubated with bacterially expressed GST-ACTN4 (WT) or with GST-ACTN4 (LXXAA) fusion proteins in the presence of 100 nm vitamin D3. Pulldown fractions were subjected to Western blotting with α-VDR -antibodies. The arrow indicates the full-length GST-ACTN4 fusion protein. Lane 1 shows 10% of the input for pulldown experiments. B, ACTN4 (LXXAA) mutant loses its ability to interact with ERα. GST pulldown assays were carried out as described in A, except ERα expression plasmids were used for transfection, and pulldowns were carried out in the presence of 100 nm of E2. Lane 1 shows 5% input. C, LXXLL motif is essential for VDR-mediated transcriptional activation. Expression plasmids for ACTN4 (WT) or the ACTN4 (LXXAA) mutant were co-transfected with or without expression plasmids for VDR along with a reporter construct harboring a VDRE in CV-1 cells. Reporter assays were carried out as described in Fig. 2B. D, ACTN4 (LXXAA) loses its ability to potentiate ERα activity. The experiment was performed as described in Fig. 2C. Each data point represents the mean and S.D. of results from triplicates.