FIGURE 9.
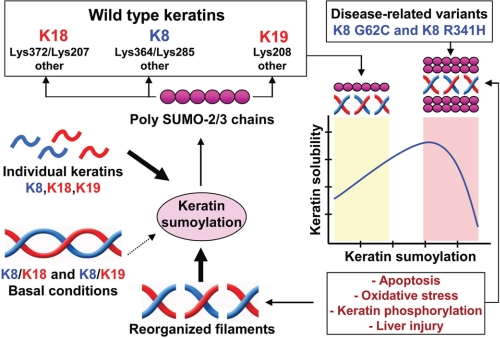
Dual role for sumoylation in regulating the solubility of wild type and disease-associated keratin mutants. K8, K18, and K19 are modified by polymeric SUMO-2/3 chains on multiple rod domain lysine residues. Wild type keratin SUMO modification is highest in the context of individually expressed keratins or upon stress- and phosphorylation-induced filament reorganization. Under basal conditions where type I/II keratin heteropolymers predominate, precluding access to SUMO target lysines, wild type keratin sumoylation is minimal. In contrast, variants of human K8 that predispose individuals to acute and chronic liver diseases, including K8 G62C and K8 R341H, are hypersumoylated under basal conditions, likely in response to post-translational modifications or structurally induced changes in filament organization. Sumoylation regulates keratin solubility, such that low level sumoylation promotes solubility, whereas hypersumoylation, which is seen during liver injury, renders keratins more insoluble.