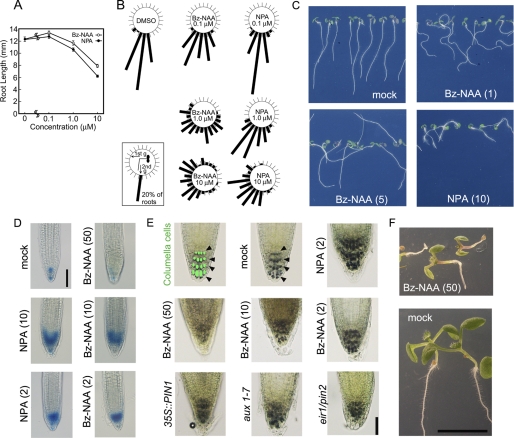
FIGURE 5.
Effects of Bz-NAA on root growth in Arabidopsis seedlings. A, root lengths. Seedlings were grown vertically on half-strength Okada and Shimura (OS) agar medium (34) with Bz-NAA (7b) or NPA for 5 days in white light at 100 μmol m−2 s−1. Data and error bars represent the mean ± S.E. (n = 95–100). B, root gravitropism. Before incubation, the seed's orientations were adjusted upwards as described previously (52). Seedlings were grown in the first gravity direction (1st g) on vertical OS agar medium with Bz-NAA or NPA under white light at a confluence rate of 50 μmol m−2 s−1. The 4-day-old seedlings were rotated at an angle of 90° (2nd g) and kept in the same white light condition for a further 24 h. The frequency (%) of root growth direction at intervals of 15° are represented by the lengths of the bars. About 90 seedlings were measured in each experiment. C, photograph of 5-day-old Arabidopsis wild-type seedlings (Col-0) grown vertically on OS agar medium containing Bz-NAA or NPA. D, histochemical staining of root tips in the Arabidopsis DR5::GUS line grown with Bz-NAA or NPA for 4 days. Scale bar represents 100 μm. E, effects of Bz-NAA and NPA on the organization of columella cells. Arabidopsis aux1–7, eir1/pin2, and PIN1-overexpressed mutants were cultured for 5 days on GM agar medium. Wild-type (Col) seedlings were grown with chemicals at the indicated concentrations for 5 days. Arrows indicate the columella cells visualized by lugol staining. Scale bar represents 50 μm. F, Arabidopsis wild-type seedling (Col) grown vertically for 6 days on GM agar medium containing Bz-NAA. Scale bar represents 5 mm. C–F, the values in parentheses present the concentration of chemicals at micromolar concentrations.