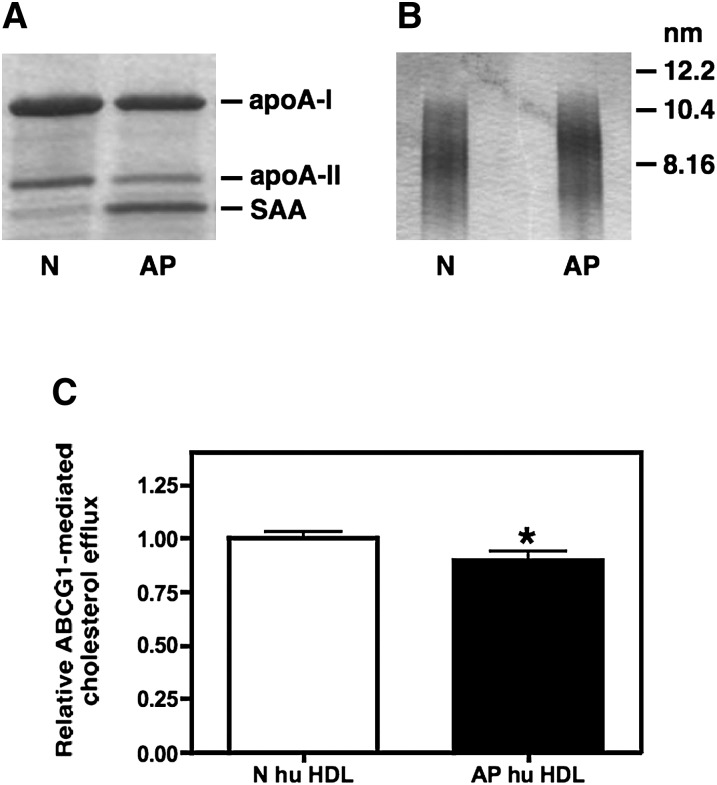
Fig. 6.
ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux to N and AP human HDL. HDL (d = 1.063-1.21 g/ml) was isolated from the plasma of normal subjects (N) or from patients 24 h post cardiac surgery (AP). Visualization was by Coomassie staining of HDL subjected to SDS-PAGE (A) and GGE (B). Transfected BHK cells were labeled with [3H] cholesterol and then induced to express ABCG1 as described in “Materials and Methods.” Cellular cholesterol efflux stimulated by 5 h incubations with 25 µg/ml N and AP human HDL was measured. ABCG1-mediated efflux was calculated as the difference between ABCG1-expressing cells and control cells that were not induced to express ABCG1 (C). Values (mean ± SEM) were obtained from eight experiments performed with three preparations of human N and AP HDL and are expressed relative to the corresponding N hu HDL. Significance was determined by Student t-test. ABCG1, ATP binding cassette transporter G1; AP, acute phase; BHK, baby hamster kidney; GGE, gradient gel electrophoresis; N, normal.