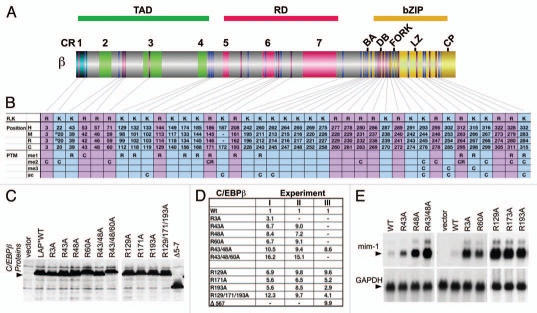
Figure 2.
Distribution, methylation, and functional evaluation of conserved arginine residues in C/EBPβ. (A) Schematic representation of the C/EBPβ structure showing the distribution of evolutionary conserved arginine (R, magenta) or lysine (K, blue) in relation to the domain and CR structure. (B) List of R and K residues in human (H) mouse (M), rat (R), and chicken (C) C/EBPβ. Numbers refer to equivalent amino acid positions. Underneath: identification by mass spectrometry and summary of data of mono-(me1), di-(me2), tri-(me3) methylation, and acetylation (ac) in rat (R) and chicken (C) C/EBPβ. (C) Protein expression controls in QT6 fibroblasts of chicken C/EBPβ LAP* arginine to alanine (R to A) mutants or wild type (WT), as indicated. (D) Reporter activation by C/EBPβ mutants. Expression constructs encoding wild type or R to A C/EBPβ mutants were transfected together with a cMGF promoter luciferase construct and reporter expression was determined after 36 hours. Numbers show reporter activation as means of duplicates from 3 independent experiments (I, II, III). (E) Endogenous gene activation by C/EBPβ mutants. RNA blots show expression of the resident myeloid C/EBP target gene mim1 in QT6 fibroblasts. C/EBPβ R to A mutants or wild type C/EBPβ LAP* were transfected and expression levels of endogenous genes were monitored by Northern blotting. GAPDH expression serves as control.