Figure 6.
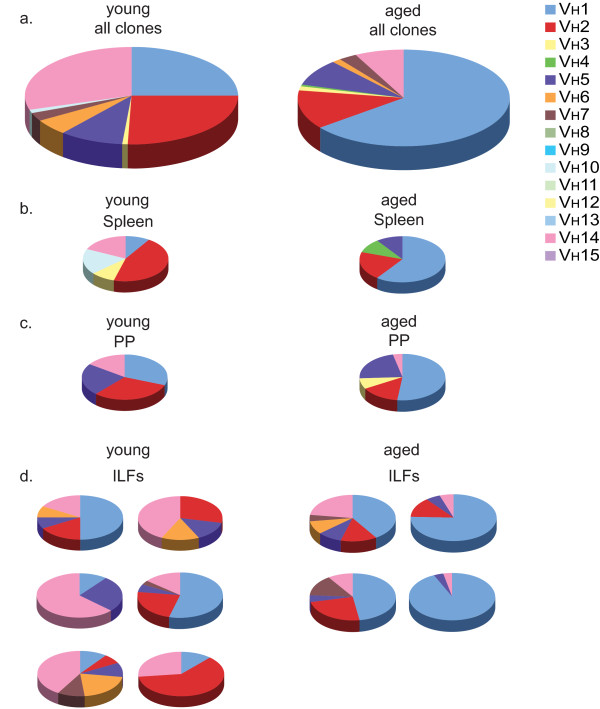
ILFs from young and aged mice contain a B-lymphocyte repertoire that is reflective of the systemic B lymphocyte pool; the B-lymphocyte repertoire becomes skewed with aging. RNA isolated from the spleen, PP, and individual ILFs from a young and aged mouse was transcribed into cDNA and immunoglobulin genes amplified using a universal VH primer and a constant IgM region primer. Gel-purified products were ligated into vectors and individual clones containing the appropriate size insert were sequenced and assigned to a VH family. Analysis of all clones identified from the young (left) and aged mice (right) revealed a similar preferential usage of VH families with VH1, VH2, and VH14 representing greater than 80% of the VH families used by either mouse (panel a). With aging, the Ig repertoire became more skewed with dominant usage of the VH1 family (panel a right). Comparison of the VH usage within the spleen (panel b), reflective of the systemic pool, to the PP (panel c) and individual ILFs (panel d) revealed similar VH usage between these tissues within aged and young mice and revealed that the Ig repertoire was skewed toward dominant VH1 usage in all tissues in the aged mouse (panels b-d right).
