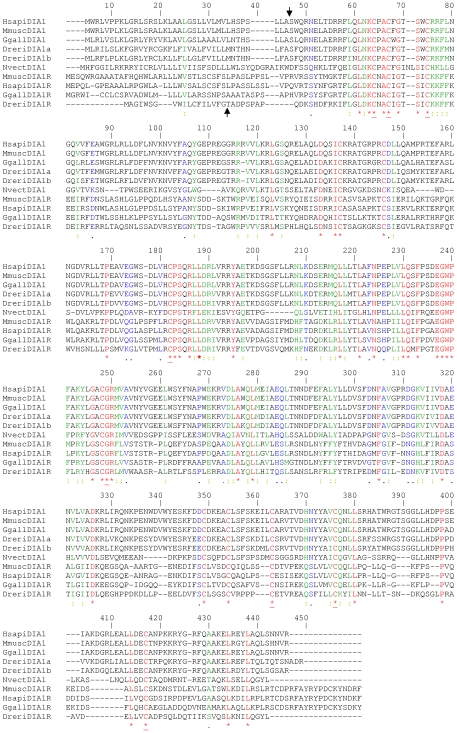
Figure 4. Amino acid sequence alignment of DIA1 and DIA1R proteins from key species.
Gene products from species with known full-length DIA1 and DIA1R orthologues were aligned using CLUSTALW [47], with DIA1 from the cnidarian species Nematostella vectensis (NvectDIA1), included for comparative purposes. Identical amino acids are highlighted in red font and indicated below the alignment with an asterisk (*). Strongly similar amino acids are highlighted in green font and indicated below the alignment with a colon (:). Weakly similar amino acids are highlighted in blue font and indicated below the alignment with a full stop (.). Dissimilar amino acids are in black font. Amino acids conserved in all DIA1 and DIA1R proteins, as determined by alignment of the DIA1 and DIA1R gene products from all species (Figure S4), are underlined (*). Amino acid numbering is provided above the alignment. Gaps required for optimal alignment are indicated by dashes. Standard single-letter amino acid abbreviations are used. Organism abbreviations use the first letter of the genus name, followed by the first four letters of the species (e.g. Homo sapiens DIA1R is abbreviated to HsapiDIA1R). Full species names and accession numbers can be found in Tables S1 and S4. Predicted signal peptide cleavage sites for human DIA1 and DIA1R (Figure S5) are indicated by arrows above or below the alignment, respectively.