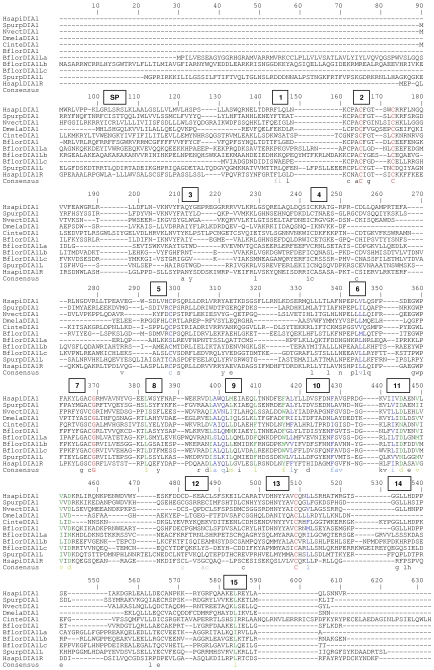
Figure 5. Amino acid sequence alignment of DIA1-family proteins from key species.
All full-length DIA1, DIA1R, and/or DIA1L gene products were aligned using CLUSTALW (Figure S7), and this figure represents excerpts from this master alignment, where proteins from the following phyla only are represented: Cnidaria (N. vectensis DIA1: NvectDIA1), Arthopoda (D. melanogaster DIA1: DmelaDIA1), Echinodermata (S. purpuratus DIA1 and DIA1L: SpurpDIA1 and SpurpDIA1L), Cephalochordata (B. floridae DIA1 and DIA1L paralogues: BflorDIA1, BflorDIA1La, b, and c), and Chordata. The latter includes representatives of the subphylum Urochordata (C. intestinalis DIA1: CinteDIA1) and subphylum Vertebrata (H. sapiens DIA1 and DIA1R: HsapiDIA1 and HsapiDIA1R). Amino acid numbering from the master alignment (Figure S7) is provided above the alignment. Gaps required for optimizing the master alignment (Figure S7) are indicated by dashes. Standard single-letter amino acid abbreviations are used. Organism abbreviations use the first letter of the genus name, followed by the first four letters of the species (e.g. Homo sapiens DIA1R is abbreviated to HsapiDIA1R). Full species names and accession numbers can be found in Tables S1, S4 and S7. The predicted location of the DIA1 and DIA1R signal peptides (SP) are indicated above the alignment (Figure S5). Conserved amino acid motifs detected in the master alignment (Table 3, Figure S7) are indicated in numbered boxes above the alignment. Consensus amino acids for each motif are indicated below the alignment. Amino acids absolutely conserved across the whole DIA1-family are indicated in red upper-case letters, those strongly conserved across the whole DIA1-family are in green, and those weakly conserved across the whole DIA1-family in blue (Figure S7). In addition, black lower-case letters indicate amino acids conserved in over 80% of DIA1-family sequences (Figure S8), while grey lower-case letters indicate conservation in 50–80% of DIA1-family sequences (Figure S9).