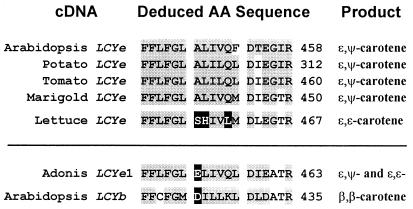
Figure 6.
A determinant of the number of ɛ-rings added to lycopene by Arabidopsis and lettuce lycopene ɛ-cyclases was mapped to a 6-aa region defined by the residues ALIVQF in the Arabidopsis ɛ-cyclase and SHIVLM in the lettuce ɛ-cyclase (see Figs. 4 and 5). Deduced amino acid sequences of lycopene mono-ɛ-cyclases from tomato (9), marigold (18), and potato (this work) are also displayed for this region. Similarly conserved residues are shown in black text on a gray background. Three amino acid residues in the lettuce bi-ɛ-cyclase that differ significantly from those in the known mono-ɛ-cyclases are in white text on a black background. Sequences of an Arabidopsis LCYb (a bicyclase) and an Adonis LCYe of mixed function are displayed below the lettuce LCYe with two residues of interest shown in white text on a black background. Similarity was defined according to the blosum 45 scoring matrix (19): DE, NH, ST, QKR, FYW, LIVM. GenBank accession nos.: Adonis LCYe1, AF321535; Arabidopsis LCYb, U50739; Arabidopsis LCYe, U50738; lettuce LCYe, AF321538; marigold LCYe, AF251016; potato LCYe, AF321537; tomato LCYe, Y14387.