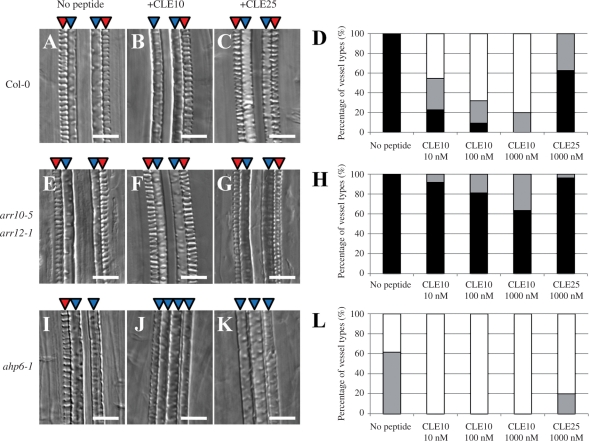
Fig. 3.
CLE10 peptide-dependent suppression of protoxylem vessel formation in mutants defective in cytokinin signaling. (A–C, E–G, I–K) The WT, arr10-5 arr12-1 and ahp6-1 seedlings were grown for 7 d on agar plates (with 0.8% agar) containing no peptide, 1 μM CLE10 and 1 μM CLE25. (D, H, L) Dose-dependent suppression of protoxylem vessel formation by CLE10. The WT (D), arr10-5 arr12-1 (H) and ahp6-1 (L) seedlings were grown for 7 d on plates with no peptide, 10–1000 nM CLE10 and 1000 nM CLE25, and classified into three types depending on the phenotype of protoxylem vessels in the primary root. Black represents normal protoxylem vessel formation where two protoxylem cell files differentiated correctly. Gray represents a weak abnormal phenotype showing that one of the two protoxylem cell files was missing or interrupted. White represents a severe abnormal phenotype showing that both protoxylem cell files were missing or interrupted. (N = 19–30). Scale bars are 25 μm.