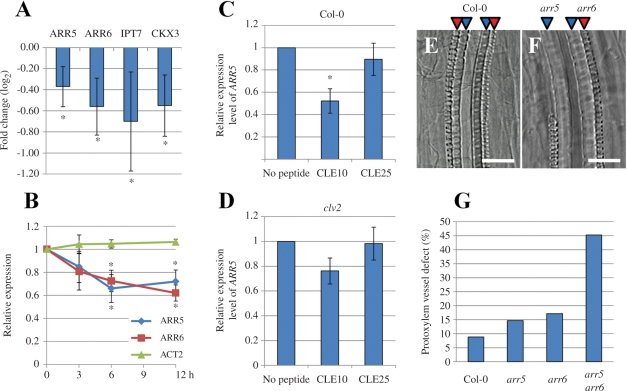
Fig. 6.
Cross-talk between type-A ARRs and CLE10 signaling in protoxylem vessel formation. (A, B) Reduction of transcript levels of cytokinin-related genes including type-A ARRs by CLE10 peptide. Arabidopsis seedlings were grown in liquid medium containing 1 μM CLE10 or 1 μM CLE25 for 3–12 h, and transcript levels of cytokinin-related genes were measured by GeneChip (A) or with quantitative PCR (B). (A) Expression levels of four genes (ARR5, ARR6, IPT7 and CKX3) were significantly decreased by 12 h treatment of CLE10. The fold change was calculated as the ratio of transcript levels of plants treated with CLE10 compared with CLE25 (in log2 scale). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.1). (B) Changes in two type-A ARR transcripts by 3, 6 and 12 h treatment of 1 μM CLE10 or CLE25. ACT2 was used as a control. The relative expression was calculated as the ratio of transcript levels of plants treated with CLE10 when compared with CLE25. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.01). (C, D) ARR5 expression levels of plants treated with no peptide, 1 μM CLE10 or 1 μM CLE25 for 6 h in the WT (C) or clv2 (D). The relative expression was calculated as the ratio of transcript levels of plants treated with CLE peptides when compared with no peptide. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences when compared with no peptide treatment (P < 0.01). (A–D) Error bars represent SD (N = 3). (E–G) Defects in protoxylem vessel formation in lateral roots. (E, F) Protoxylem vessel formation in lateral roots of 8-day-old WT and arr5 arr6 seedlings. (G) The frequency of suppressed protoxylem vessel formation in lateral roots of WT, arr5, arr6, arr5 arr6 (N = 32–53). One to four lateral roots located next to the hypocotyl, per seedling, were used for measurement. Scale bars are 25 μm.