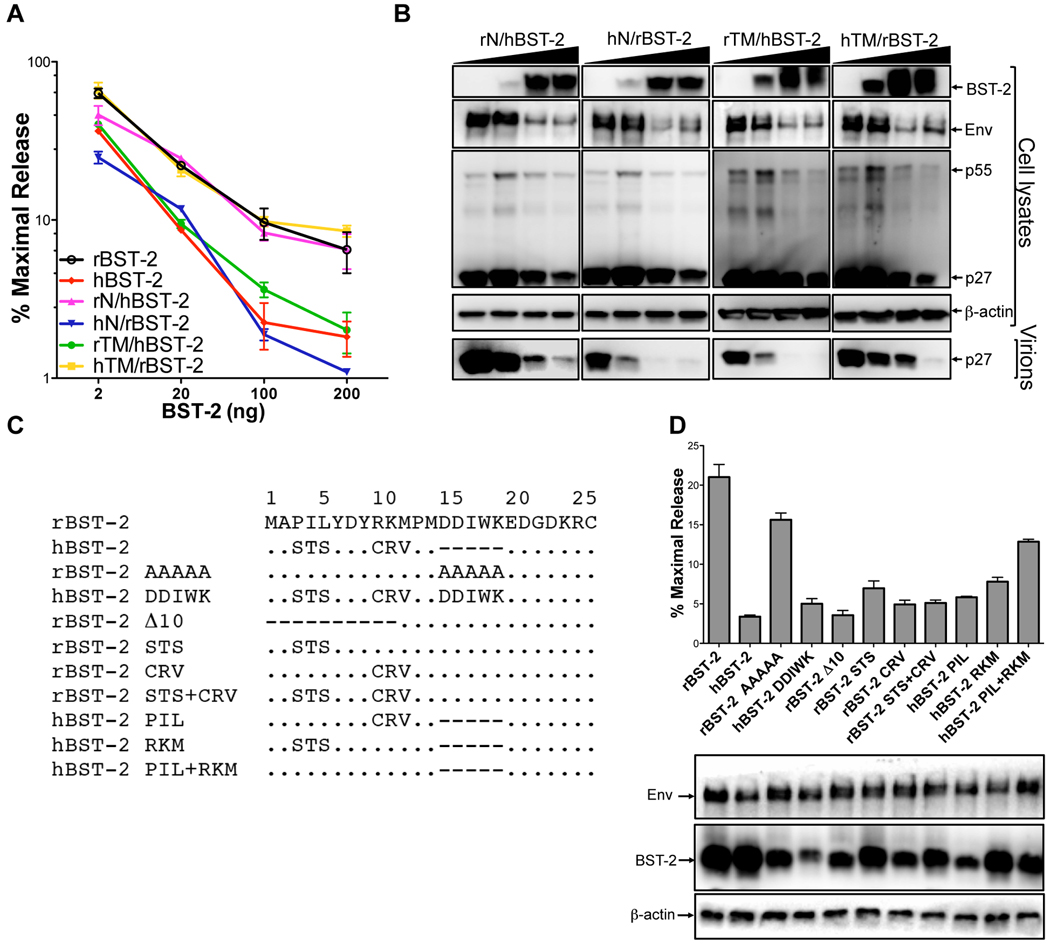
Figure 5. Identification of residues in the cytoplasmic domain of rhesus tetherin that confer susceptibility to SIV ΔnefP.
Sequences coding for the cytoplasmic (N) and transmembrane (TM) domains of human and rhesus tetherin (rBST-2 and hBST-2) were exchanged to generate expression constructs for the following recombinants; rN/hBST-2, hN/rBST-2, rTM/hBST-2 and hTM/rBST-2. Virus release from 293T cells co-transfected with SIV ΔnefP proviral DNA and increasing amounts of each of the tetherin recombinants (2, 20, 100 and 200 ng) was determined by p27 antigen-capture ELISA (A) and verified by western blot analysis (B). (C) The indicated amino acid substitutions and deletions were introduced into the cytoplasmic domains of rhesus and human tetherin. (D) These mutants were tested for the ability to inhibit virus release for SIV ΔnefP. The expression of Env and each of the tetherin mutants was verified by western blot analysis of cell lysates. (A and D) Error bars indicate the standard deviation (+/−) of mean percent maximal virus release.