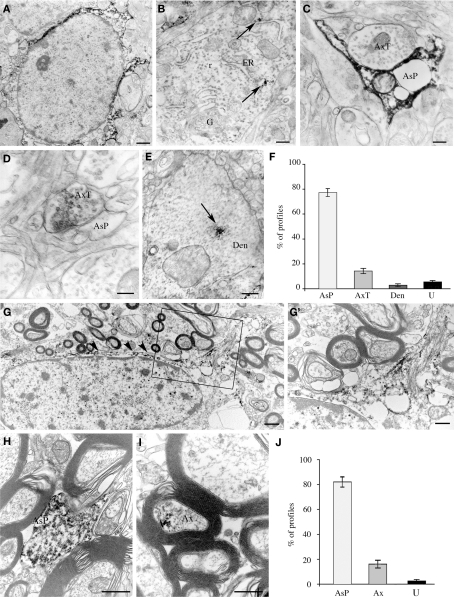
Figure 5.
Cellular localization of EAAT2a-ir in human cerebral cortex studied by pre-embedding electron microscopy. (A–E) In gray matter, EAAT2 ir is localized to astrocytes (A) and rarely in neurons (B), where it is closely associate to endoplasmic reticulum (arrows). In the neuropil, EAAT2a is observed in astrocytic processes (C), axon terminals (D), and dendrites (E). Area 10; case HBC 980611. (F) Quantification of EAAT2a+ profiles in gray matter. (G–I) In white matter, EAAT2 ir is in fibrous astrocytes [arrowheads in (G)] and along their fibrous processes [(G′); enlargement from the framed region in (G)], in astrocytic processes (H) and in myelinated axons (I). Area 10; case HBC 981115. (J) Quantification of EAAT2a+ profiles in white matter. Ax, myelinated axon; AxT, axon terminal; AsP, astrocytic process; Den, dendrite; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; f, astrocyte fibrous filament; G, Golgi apparatus; r, ribosomes; U, unidentified profiles. Scale bars: 0.8 μm for (A,G); 0.1 μm for (B); 0.25 for (C); 0.15 μm for (C,D); 0.3 μm for (G′,I); and 0.4 for μm (J).