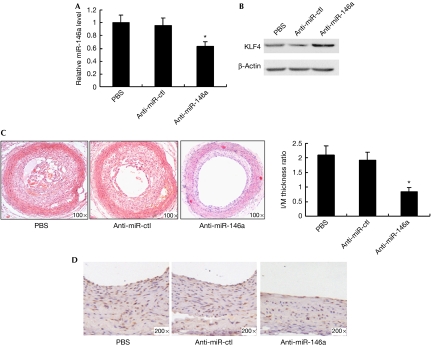
Figure 4.
miR-146a promotes vascular neointimal hyperplasia in vivo. (A) miR-146a expression in carotid arteries from PBS-, anti-miR-ctl (33 μg)- and anti-miR-146a (33 μg)-treated rats at 14 days after balloon injury, as detected by qRT–PCR. *P<0.05 compared with PBS and anti-miR-ctl control. (B) Western blotting for KLF4 expression in carotid arteries from PBS-, anti-miR-ctl- and anti-miR-146a-treated rats at 14 days after balloon injury. (C) Haematoxylin–eosin staining of carotid arteries from PBS-, anti-miR-ctl- and anti-miR-146a-treated rats at 14 days after balloon injury. Neointimal formation was calculated as the I/M ratio. *P<0.05 compared with PBS and anti-miR-ctl control. (D) PCNA immunohistochemical staining of carotid arteries from PBS-, anti-miR-ctl- and anti-miR-146a-treated rats at 14 days after balloon injury. I/M, intima/media; KLF, Krüppel-like factor; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; qRT–PCR, quantitative real-time PCR.