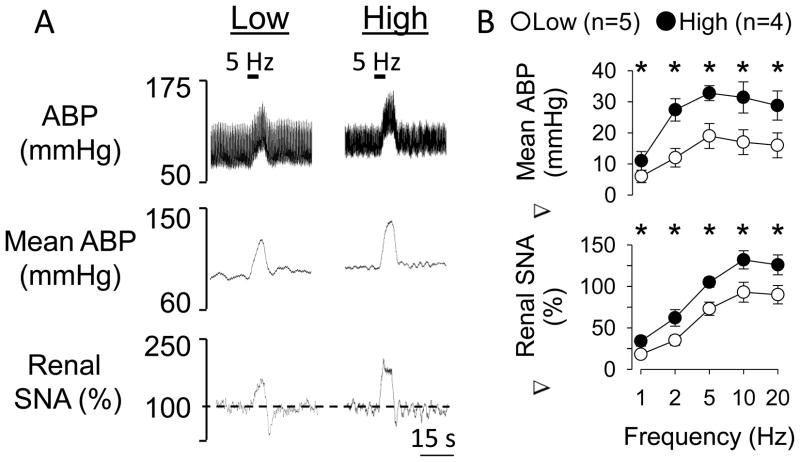
Figure 3.
Elevated dietary salt intake enhances renal sympathetic nerve activity and ABP responses to electrical activation of sciatic nerve afferents. (A) Representative examples of ABP, mean ABP, and integrated and rectified renal sympathetic nerve activity in rats drinking water (low) or 0.9% NaCl (high) for 14 days during electrical stimulation of sciatic nerve afferents (500 uA, 1 ms pulse duration). (B) Mean ± SEM of the change in mean ABP and renal sympathetic nerve activity during electrical stimulation of sciatic nerve afferents of rats drinking water or 0.9% NaCl for 14 days. *Significant difference between low and high salt rats (P<0.05)