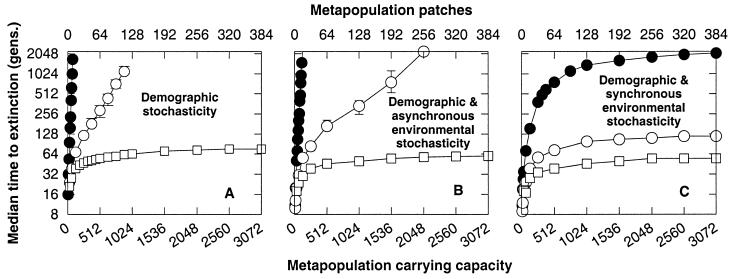
Figure 4.
The time to extinction for a metapopulation with (A) demographic stochasticity, (B) demographic and spatially asynchronous environmental stochasticity, and (C) demographic and spatially synchronous environmental stochasticity. Globally dispersing metapopulations without mutation are denoted (●). Metapopulations with mutation accumulation are denoted (○, global dispersal; □, nearest-neighbor dispersal). The carrying capacity of a patch, K = 8. For B, K is lognormally distributed with CV(K) = 0.2. Spatially asynchronous environmental stochasticity is modeled by independently sampling K for each patch, each generation. For C, K is lognormally distributed over time, with CV(K) = 0.2. Spatially synchronous environmental stochasticity is modeled by sampling a single value of K for all patches, once per generation. Polygynous mating, fecundity R = 10. The homozygous (heterozygous) mutational effect, s = 0.05 (0.017). See Fig. 3 for initial conditions.