Figure 5.
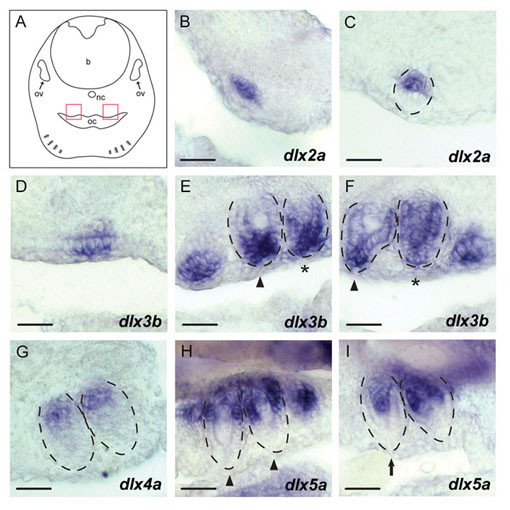
A. burtoni dlx expression patterns in pharyngeal tooth development. Transverse sections were produced after performing whole mount in situ hybridization on 8 dpf A. burtoni embryos. Dorsal is to the top. (A) Schematic illustration of a transverse view. Red boxes indicate the regions of tooth development on the upper pharyngeal jaw magnified in B-I. Outlines of developing teeth were delineated with dotted lines based on hematoxilin-eosin staining performed after photographing these sections. (B, C) dlx2a expression. The signal in the dental mesenchyme was observed in a short period of early tooth development including morphogenesis stage (B, C). (D-F) dlx3b expression in the developing teeth. The signal was observed in the dental mesenchyme and oral epithelium during morphogenesis (D). The signal in the dental mesenchyme persisted until early differentiation (asterisks in E and F). In a later stage, the expression became more restricted towards the tip of the developing teeth (arrowheads in E and F). (G) dlx4a expression. The expression signal was observed at the base of the differentiating teeth in the dental mesenchyme and epithelium. (H, I) dlx5a expression. This gene was expressed more intensively in the dental epithelium than in the mesenchyme at the base of the differentiating teeth (arrowheads in H). Teeth in a later phase of differentiation showed intense mesenchymal expression signals compared with epithelial expression, which was restricted to the base of the inner dental epithelium (arrow in I). Developmental staging of teeth was based on Figure 4 of [32] for basic description in medaka and Figure 1 of [62] for that in a cichlid fish. Abbreviations: ov = otic vesicle; nc = notochord; b = brain; oc = oral cavity. Anteroposterior levels of these photos are indicated in Additional file 9. Scale bar: 20 μm.
