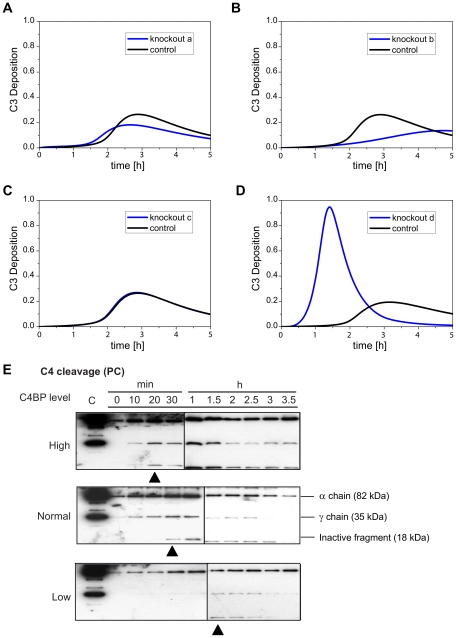
Figure 6. Knockout simulations reveal the major role of C4BP.
(A) Simulation profiles of C3 deposition with or without reaction a. (B) Simulation profiles of C3 deposition with or without reaction b. (C) Simulation profiles of C3 deposition with or without reaction c. (D) Simulation profiles of C3 deposition with or without reaction d. Reactions (a–d) are labeled red in Figure 1A and explained in the caption: (a) C4BP binds to CRP, (b) C4BP binds to C4b, (c) C4BP prevents the assembly of C4bC2a, and (d) C4BP accelerates the decay of the C4bC2a,. (E) Experimental verification. Profiles of deposited cleaved/uncleaved C4 fragments across time points of 0–3.5 h under infection-inflammation condition occurring via classical pathway (triggered by PC beads) in untreated or treated sera with increased C4BP or decreased C4BP were studied. The black triangles point to the first appearance of inactive fragments.