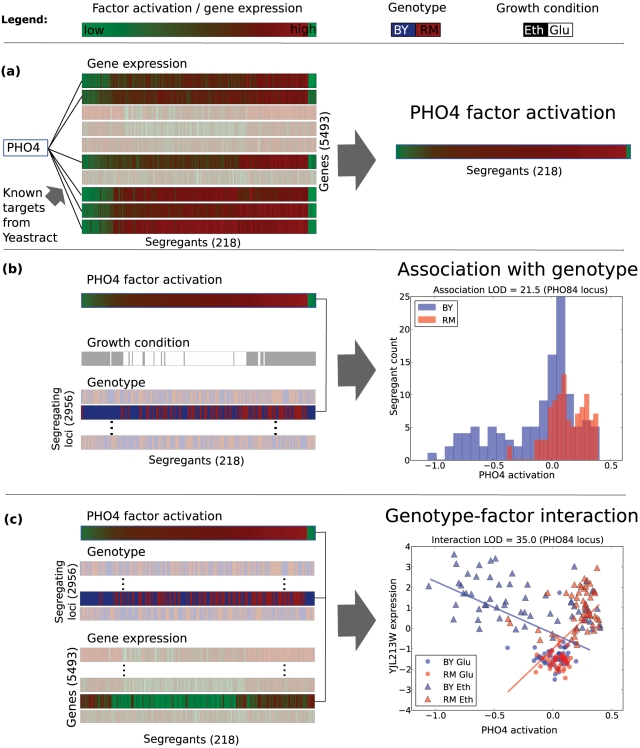
Figure 1. Analysing genetic effects in the context of intermediate phenotypes using PHO4 as an example.
(a) Intermediate phenotypes are learnt from expression levels using prior information from Yeastract database on the targets of the factor. The highlighted genes are known targets of PHO4. These activations are learned jointly for all factors. (b) The variation in intermediate phenotypes can be explained by locus genotypes or the growth condition of the segregants. For most loci (greyed out), the genotype is uncorrelated with the factor activation level. For the PHO84 locus at chrIII-46084, not greyed out and indicated by arrow, it is correlated. The plot at right shows the distribution of factor activations stratified by genotype at this locus. (c) Some genotypes show a statistical interaction with the inferred intermediate phenotype affecting gene expression levels, in this case YJL213W. See also Figure 2.