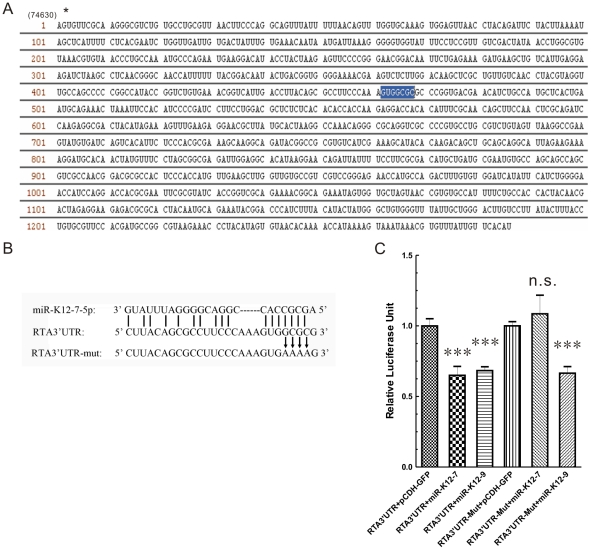
Figure 2. The seed-match site is essential for the regulation of RTA by miR-K12-7-5p.
(A) The type I RTA 3′UTR (nt 1–1286) contains one perfect seed-match site (highlighted). *74630 indicate the starting site position in the KSHV genome (accession number: U75698). (B) Potential base pairing between miR-K12-7-5p and its predicted pairing site in RTA3′UTR. Watson–Crick base pairs are indicated with vertical lines. The mutations made in the 3′UTR are shown below the wild-type sequences. (C) Site-directed mutagenesis demonstrates that the seed match site is essential for the regulation of RTA expression by miR-K12-7-5p. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with 50 ng pGL3–RTA3′UTR or pGL3–RTA3′UTR-mut and 1 µg miR-K12-7 or miR-K12-9 expression construct, or the corresponding empty vector. pRL–SV40 (4 ng) was transfected as the internal control. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h after transfection. The data shown are from six independent transfections. ***P<0.001; n.s., not significant, t-test.