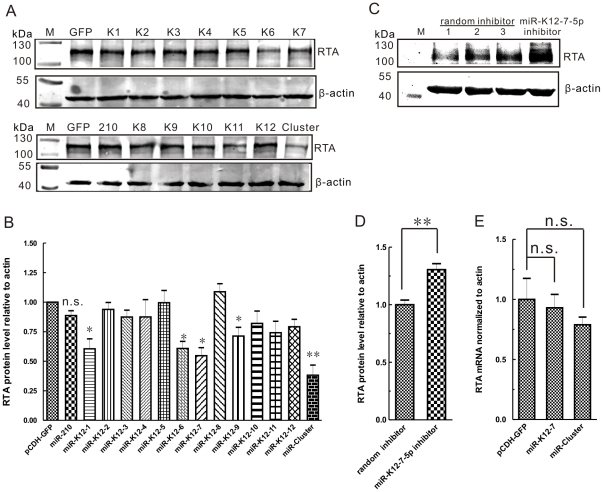
Figure 3. miR-K12-7 inhibits RTA expression at the protein level but not at the mRNA level.
(A) The transient expression of miR-K12-7 repressed RTA protein expression in the latently KSHV-infected 293/Bac36 cell line. Latently KSHV-infected 293/Bac36 cells were synchronized by culture in serum-free medium and pretransfected with 4 µg of individual miRNA-expressing constructs or the corresponding empty vector 12 h after the addition of serum. After a further 4 h, the S-phase 293/Bac36 cells were induced to lytic replication with both TPA (25 ng/mL) and VPA (3 mM). Cell lysates were prepared 26 h after induction and were probed for endogenous RTA or β-actin. (B) A graph of RTA levels normalized to those of β-actin of three independent experiments performed in Figure 3A (analyzed with NIH ImageJ). (C) miR-K12-7-5p inhibitor increases RTA expression. Synchronized 293/Bac36 cells were transfected with 200 nM miR-K12-7-5 inhibitor or random inhibitor and were introduced into lytic replication with both TPA (25 ng/mL) and VPA (3 mM). Cell lysates were prepared 48 h after induction and were probed for endogenous RTA or β-actin. (D) A graph of RTA levels normalized to those of β-actin of three independent experiments performed in Figure 3C (analyzed with NIH ImageJ). (E) RTA mRNA levels were not affected by miR-K12-7. At 26 h after induction with TPA and VPA, the 293/Bac36 cells transfected with individual miRNA expression constructs or the corresponding empty vector were harvested and RNAs were extracted from those cells with TRIzol Reagent. RTA mRNA from those cells was assayed by RT–PCR and quantified relative to β-actin mRNA levels. The data shown are from triplicate independent experiments. *P<0.05; ** P<0.01; n.s., not significant. t test.