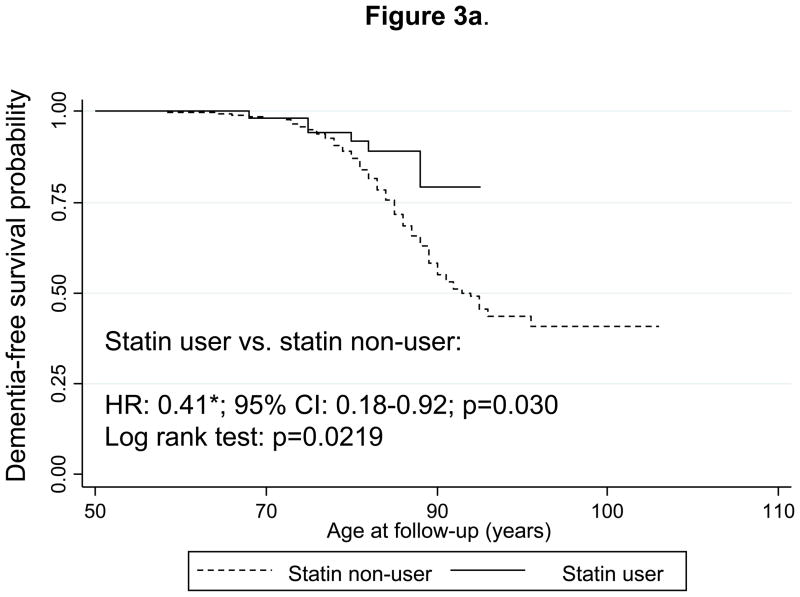
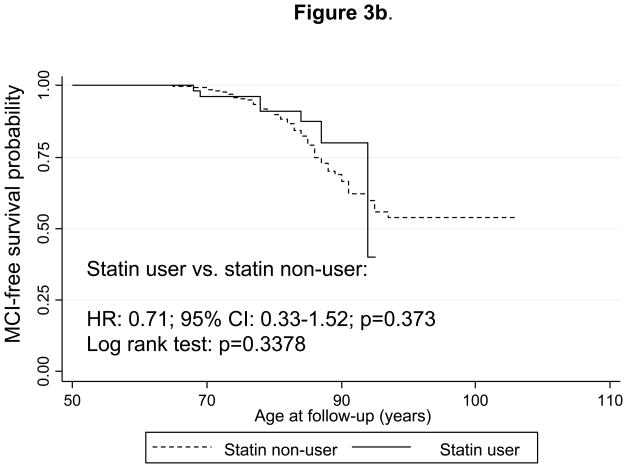
Figure 3.
Figure 3a. Kaplan-Meier survival curve of time to incidence of dementia by use of statins (time-dependent): Cox Proportional Hazards model and Log-rank test.
Notes: A participant is defined as a statin user at first prescription onwards, prior to onset of dementia or MCI or by end of follow-up if a non-case but beyond age 50 years. Cox PH model analysis controlled for the same covariates as in Figure 1a, but was based on 1,560 participants at risk for dementia and for use of statins (visits at or after 1985) and 252 dementia failures (person-years=37842). Log-rank test was based on 259 incident cases. Six statin-users were observed incident dementia cases, while 14.3 were expected to become incident cases by chance, which yielded a Log-rank χ2 test of 5.26 (1 d.f.); p=0.0219.
*p<0.05 for null hypothesis that Loge(HR)=0.
Figure 3b. Kaplan-Meier survival curve of time to incidence of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by use of statins (time-dependent): Cox Proportional Hazards model and Log-rank test.
Notes: Statin use was defined the same way as in Figure 2a. Cox PH model analysis controlled for the same covariates as in Figure 1a, but was based on 1,308 subjects at risk for MCI and for use of statins (visits at or after 1985) and 133 failures (person-years= 29,600). Log-rank test was based on 138 incident cases. Seven statin-users were observed incident MCI cases, while 9.9 were expected to become incident cases by chance, which yielded a Log-rank χ2 test (1 d.f.) of 0.92; p=0.3378.