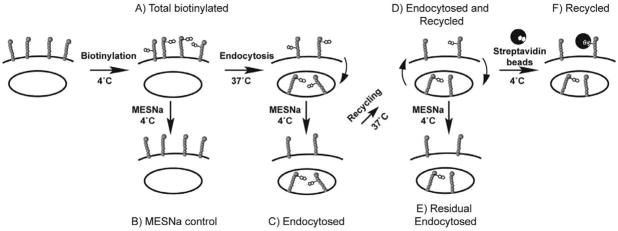
Figure 7. Schematic summary of internalization and recycling assays with biotinylated CD22.
Endocytosis Assay: A) Cells are labeled with a cell-impermeable, reversible biotinylating reagent (sulfoNHS-SS-biotin) at 4° C. B) Cells are warmed to 37° C to induce endocytosis. C) At 4° C, cells are treated with the cell-impermeable reducing agent, mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (MESNa), to remove surface biotinylation. Cells can be lysed, immunoprecipitated with streptavidin-agarose, and analyzed by western blotting at this stage to measure internalization. Recycling Assay to detect the return of MESNa-sensitive CD22: D) Cells are warmed a second time to allow return of recycling proteins to the cell surface. E) Cells are treated a second time with MESNa to remove biotin from recycled proteins, then are lysed, immunoprecipitated with streptavidin-agarose beads, and analyzed by western blotting. Loss of signal following second MESNa treatment indicates recycling. Recycling Assay Using Cell Surface Capture: F) After the second warming step, instead of a second MESNa treatment, cell surface biotinylated proteins (recycled) are isolated by streptavidin-coated magnetic beads at 4 °C. After quenching excess binding sites with biotin, cells are lysed, and bead-bound proteins are analyzed by western blotting. Recovery of the signal indicates recycling.