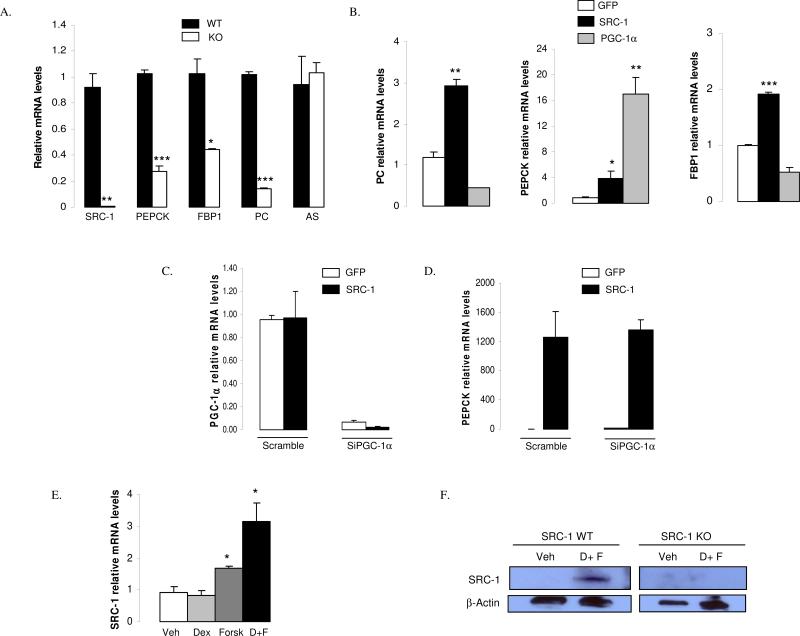
Figure 4. SRC-1 controls gluconeogenic genes in a cell-autonomous manner.
A) mRNA levels for several important gluconeogenic genes are decreased in primary hepatocytes from SRC-1 KO mice. AS: argininosuccinate synthetase
B) SRC-1 controls gluconeogenic genes that are not responsive to PGC-1α. Primary hepatocytes were treated with SRC-1 or PGC-1α adenoviruses and studied 48 hours after viral treatment. The gene expression level of specific target genes was evaluated by qPCR.
C-D) Specific knock-down of PGC-1α does not influence the activation of PEPCK by SRC-1. The mRNA levels of PGC-1α were decreased via SiRNA in Hepa1.6 cells and then over-expressed by SRC-1 using adenoviruses during 48h. The gene expression level of PEPCK was evaluated by qPCR
E) SRC-1 mRNA levels (measured by qPCR) are increased in WT hepatocytes by 24 hours of exposure to dexamethasone or forskolin or dexamethasone + forskolin.
F) SRC-1 protein levels increase in hepatocytes treated with dexamethasone + forskolin. SRC-1 protein levels were measured by immunoblot (western) analysis in hepatocytes from SRC-1 KO and WT littermates following 24 hours of treatment with dexamethasone and forskolin. D: dexamethasone; F: forskolin
Data are represented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Unpaired student's t-test was used for evaluation of statistical significance. One asterisk indicates p < 0.05; two asterisks indicate p < 0.01 and three asterisks indicate p < 0.005.
“See also Fig.S3”