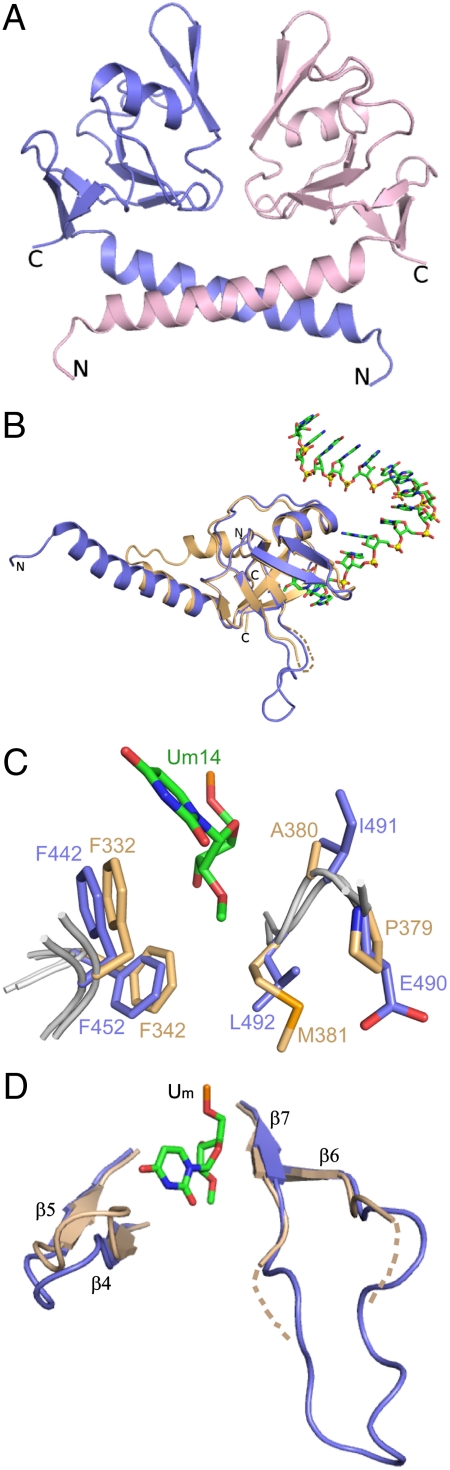
Fig. 3.
Structure of Hili PAZ in the free state and comparison of its binding pocket with Hiwi1 PAZ in RNA-bound state. (A) A view of the crystal structure of Hili PAZ in the free state. Two Hili-PAZ molecules (one in blue and the other in pink) form a symmetrical dimer mediated by helix–helix interactions between N-terminal α-helical segments. (B) Structural superposition of the PAZ domains of Hili PAZ in the free form (in blue) and Hiwi1 PAZ (in biscuit) bound to RNA (in green). (C) Structural superposition of binding pockets of Hili PAZ in the free form (in blue) and Hiwi1 PAZ (in biscuit) bound to RNA. The Um14 residue at the 3′ terminus of the RNA in the complex is shown in green. (D) A view of the relative arrangements of β6-β7 strands and β4-β5 strands of Hili PAZ (in blue) in the free state and Hiwi1 PAZ (in biscuit) in the RNA-bound complex. The 2′-OCH3-modified Um14 residue in the Hiwi1 PAZ-RNA complex is shown in green.