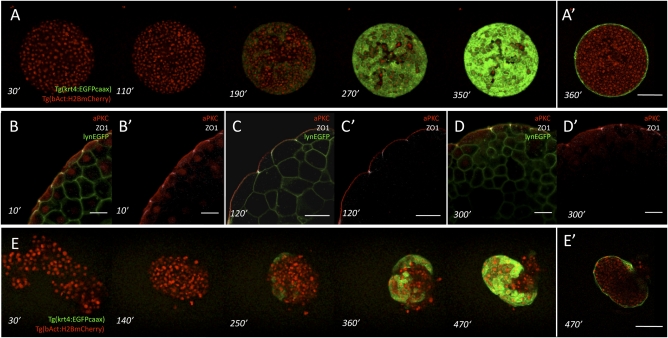
Fig. 1.
Surface cell differentiation in zebrafish germ-layer explants and aggregates. (A and A′) Time course of surface cell differentiation in ectoderm explants from Tg(krt4:EGFPcaax)/Tg(βactin:H2AmCherry) transgenic embryos expressing EGFP (green) in differentiating enveloping cell-layer (EVL) cells and mCherry (red) in all nuclei. Z projections of a representative explant at consecutive time points (A) and a single confocal section (A′) through the explant shown at the last time point. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) Time labels indicate minutes after preparation of the explants from high-to-oblong–stage embryos [3 and 5 h postfertilization (hpf)]. (B–D) Immunostaining of ectoderm explants using antibodies against atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) (apical membrane, red) and Zona Occludens 1 (ZO-1) (tight junctions, white). The plasma membrane is labeled with lynEGFP (green). (Scale bars: 25 μm.) (E and E’) Time course of surface cell differentiation in ectoderm aggregates from Tg(krt4:EGFPcaax)/Tg(βactin:H2AmCherry) transgenic embryos expressing EGFP (green) in differentiating EVL cells and mCherry (red) in nuclei. Z projections of a representative aggregate at consecutive time points (B) and confocal section through the aggregate shown at the last time point (B’). (Scale bar: 100 μm.) Time labels indicate minutes after dissociation of high-to-oblong–stage embryos (3 and 5 hpf).