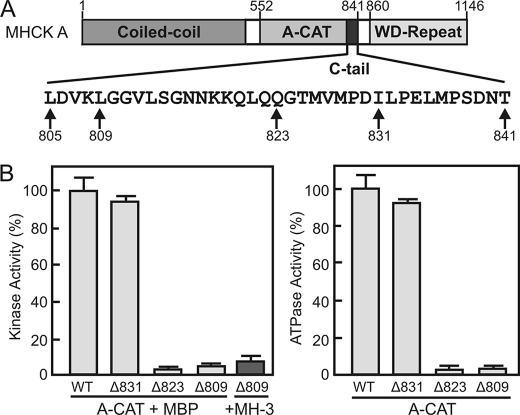
FIGURE 1.
Truncation of the C-tail inhibits the kinase and ATPase activities of A-CAT. A, schematic diagram showing the domain organization of MHCK A. A-CAT encompasses the entire α-kinase domain and part of the unstructured sequence (C-tail) linking the WD-repeat domain. The amino acid sequence of the C-tail is shown with the experimental sites of truncation indicated. B, the kinase (left panel) and ATPase (right panel) activities of wild-type A-CAT (WT) and A-CAT truncated at residues 831 (Δ831), 823 (Δ823), or 809 (Δ809) were determined. Removal of residues 823 to 831 from the C-tail resulted in a large decrease in kinase and ATPase activities. Activities were determined from time courses performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” using either MBP or the MH-3 peptide as substrate as indicated. Activities are reported as a percentage of the wild-type activity. Error bars represent the standard deviation.