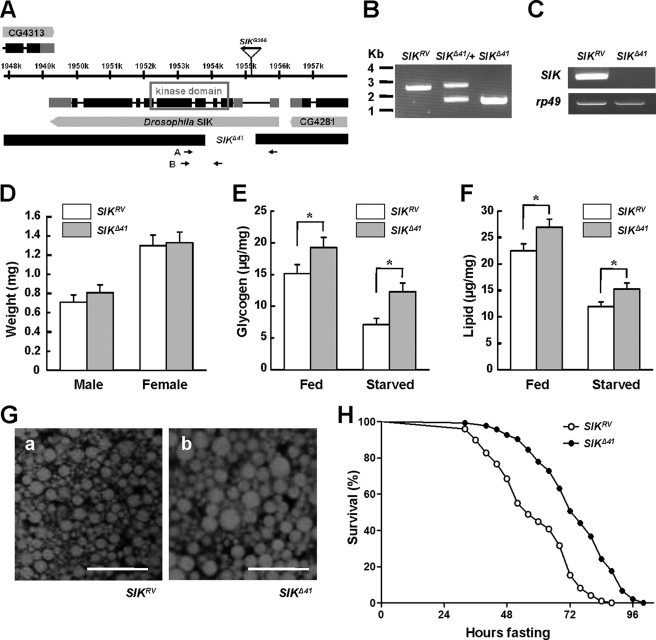
FIGURE 1.
SIK mutants are resistant to starvation. A, genomic region of SIK locus. Exons of SIK are indicated by boxes, and coding regions are colored black. The deleted regions for SIK-null mutants (SIKΔ41) are also presented. The gene expression of CG4313 and CG4281 is not affected in SIKΔ41 deletion (data not shown). B, PCR revealed deletion of genomic DNA in SIK revertants (SIKRV), heterozygous SIK mutants (SIKΔ41/+), and SIKΔ41 using the A primer set in A. C, RT-PCR analysis of SIK mRNA in SIKRV and SIKΔ41 using the B primer set in A. rp49 was used as a loading control. D, average weight of SIKRV and SIKΔ41 adult flies (mean ± S.D., n = 60). E, total glycogen contents, expressed as μg/mg of body weight, in fed or 24-h starved SIKRV and SIKΔ41 flies (mean ± S.D., n = 10; *, p < 0.05, Student's t test). F, total lipid contents in fed and 24-h starved SIKRV and SIKΔ41 flies (mean ± S.D., n = 10; *, p < 0.05, Student's t test). G, Nile Red staining of fat bodies from SIKRV (panel a) and SIKΔ41 (panel b) flies. Scale bar, 50 μm. H, relative survival rate in response to starvation of SIKRV and SIKΔ41 female flies. The percentage of survival at different times is shown. n = 60; p < 0.05 (log rank test). Experiments were performed in triplicate.