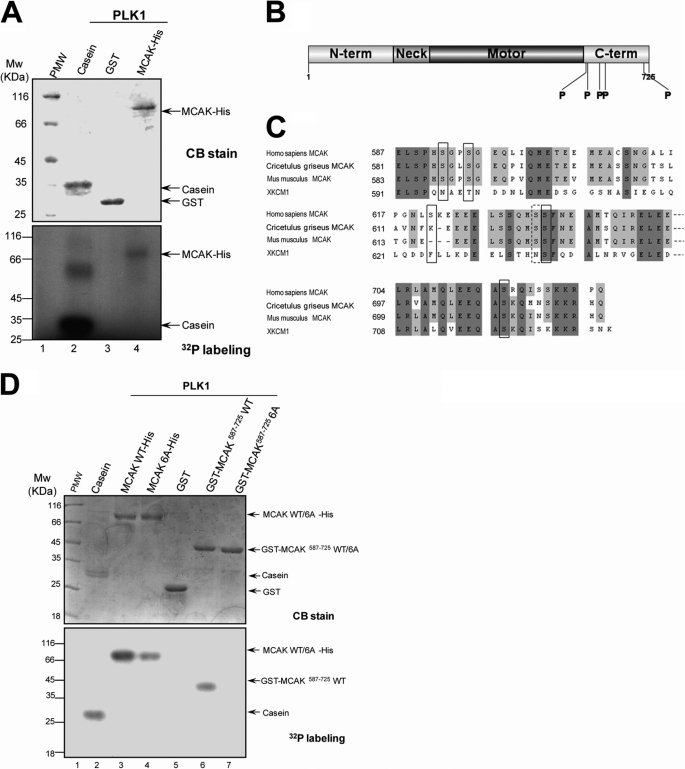
FIGURE 3.
PLK1 kinase phosphorylates MCAK protein in vitro. A, bacterially recombinant MCAK-His and GST were incubated with insect cell recombinant PLK1 kinase in an in vitro phosphorylation reaction as described under “Materials and Methods.” Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CB) to ensure equal amounts of MCAK-His and GST used in the reactions. The gels were then dried and exposed to an x-ray film. B, schematic illustration of sites of MCAK phosphorylated by PLK1. Recombinant MCAK-His and GST-MCAK(587–725) were phosphorylated by PLK1 in vitro in the absence of [γ-32P]ATP as described under “Materials and Methods,” and phosphorylation sites on MCAK were identified by mass spectrometry. Five phosphorylation sites (Ser592, Ser595, Ser621, Ser633, and Ser715) identified were shown with the boldface P. C, alignment of sequences around the phosphorylation sites for MCAK from human, Chinese hamster (CHO), mouse, and African Clawed Toad (Xenopus). Dark and light shading indicate the identical and conserved residues, respectively. The residues in the black squares indicate the phosphorylation sites. Although the residue Ser632 in the dotted square was not identified by mass spectrometry, it was also mutated in the following experiments as it is in the vicinity of the phosphorylation site Ser633. The numbers indicate the amino acid positions. D, recombinant MCAK-His (WT and its mutants) and GST-MCAK deletion mutants were phosphorylated by PLK1 in vitro as described in A.