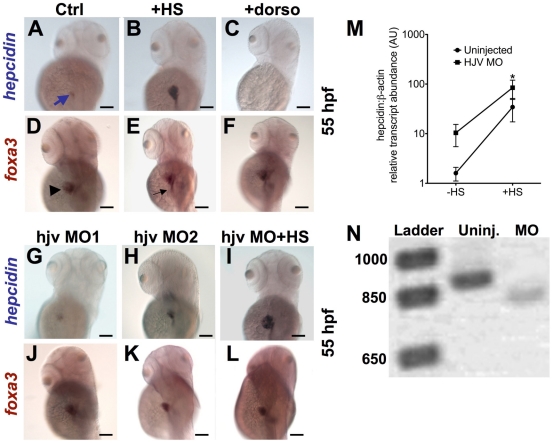
Figure 3. Knockdown of hjv does not significantly impair hepcidin expression at 55 hpf.
A–L. Whole mount in situ hybridization at 55 hpf for hepcidin (blue arrow) (A–C, G–I) and foxa3 (D–F, J–L), as a marker for the liver (arrowhead) and intestine (black arrow). Compared to controls (A,D), induction of bmp2b by heat shock in tg(hsp70: bmp2b) embryos (B,E) increased hepcidin expression. Treatment with dorsomorphin from 28–55 hpf in WT embryos abrogated hepcidin expression, without affecting liver size (C,F). Knockdown of hjv by a morpholino blocking translation (G,J), or by a non-overlapping morpholino targeting a splice acceptor site (H,K), did not significantly change hepcidin expression, but slightly reduced liver size. Knockdown of hjv in tg(hsp70:bmp2b) embryos failed to prevent strong hepcidin expression following induction of bmp2b (I,L). N = 10–30 embryos per group. M. The effect of hjv knockdown on bmp2b-induced hepcidin transcript levels assessed by quantitative realtime RT-PCR. Embryos were injected with hjv MO2 at the one-cell stage followed by heat shock (HS) at 48 hpf and fixation for RNA extraction at 55 hpf. N. Electrophoresis of RT-PCR products, which were designed to amplify the targeted splice site, confirmed an 80 basepair alteration in transcript size, consistent with aberrant splicing of the hjv transcript in the morphants.