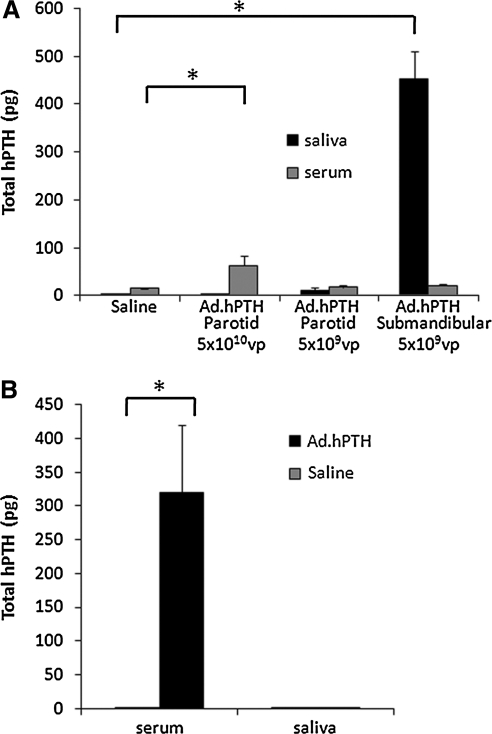
FIG. 2.
Production of transgenic hPTH from transduced salivary glands. Two days after Ad.hPTH vector infusion, blood and saliva were collected and assayed for hPTH by ELISA. Total hPTH secreted, that is, detected in serum and saliva (calculated as described in Materials and Methods), is displayed as means ± SEM. In intact animals (A, n = 6 per group), vector infusion (5 × 109 VP per gland) into both submandibular glands led to abundant detection of hPTH in the saliva and low levels in serum (saliva-to-serum ratio, 70). However, at this same dose, little transduction of parotid glands occurred. When both parotid glands were administered the higher dose (5 × 1010 VP per gland) used in this experiment, there was significant secretion of hPTH into the serum, with little hPTH found in saliva (ratio, 0.04). At a dose of 1011 VP per gland in PTX animals (B, n = 8 per group), hPTH secretion was directed specifically toward the bloodstream (ratio, 0.004). No hPTH was detected in serum or saliva of control (saline-administered) animals. *p < 0.01.