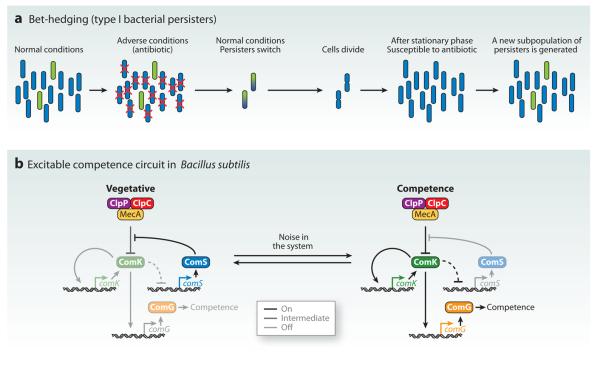
Figure 1.
Stochastic bet-hedging in bacteria generates population diversity. (a) Type I bacterial persisters. A small, stochastic subpopulation of dormant persisters survive adverse conditions. Upon return to normal growth conditions, these cells divide and reestablish the population. Finally, a new persister subpopulation is determined. (b) The DNA uptake competence cycle in Bacillus subtilis. Noise within the system drives the transition from the vegetative state to the competent state.