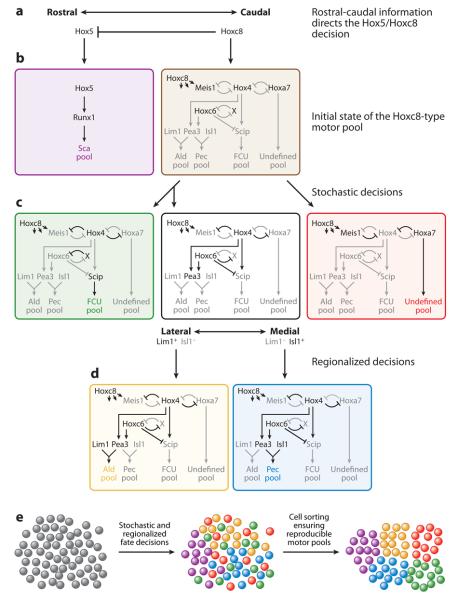
Figure 4.
Neuronal migration compensates for stochastic cell fate specification mechanisms to yield robust motor pools. (a) Rostral/caudal gradients of retinoic acid, fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and Gdf11 (a TGFβ family member) determine expression of Hox5 rostrally and Hoxc8 caudally. (b) Hox5 determines the scapulohumeralis posterior (Sca) muscle motor pool (purple). Hoxc8-expressing cells coexpress several Hox genes before undergoing additional stochastic and directional specification steps (brown). (c) The Hoxc8-expressing cells stochastically choose between expression of Hox4 or Meis1/Hoxa7. Hox4-expressing cells undergo a second stochastic decision to express Hoxc6 or not. Hox4+ Hoxc6− cells are specified as the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) pool (green). Hox4+ Hoxc6+ cells undergo an additional directed specification step (black). Meis1/Hoxa7-expressing cells determine an undefined motor pool (red). (d) Directed regionalization mechanisms determine Lim1 or Isl1 expression in Hox4+ Hoxc6+ cells. Lim1-expressing cells are specified as the anterior latissimus dorsi (Ald) motor pool (yellow). Isl1-expressing cells are specified as the pectoralis muscle (Pec) motor pool (blue). (e) Stochastic cell fate specification is compensated for via neuronal migration into coherent motor pools.