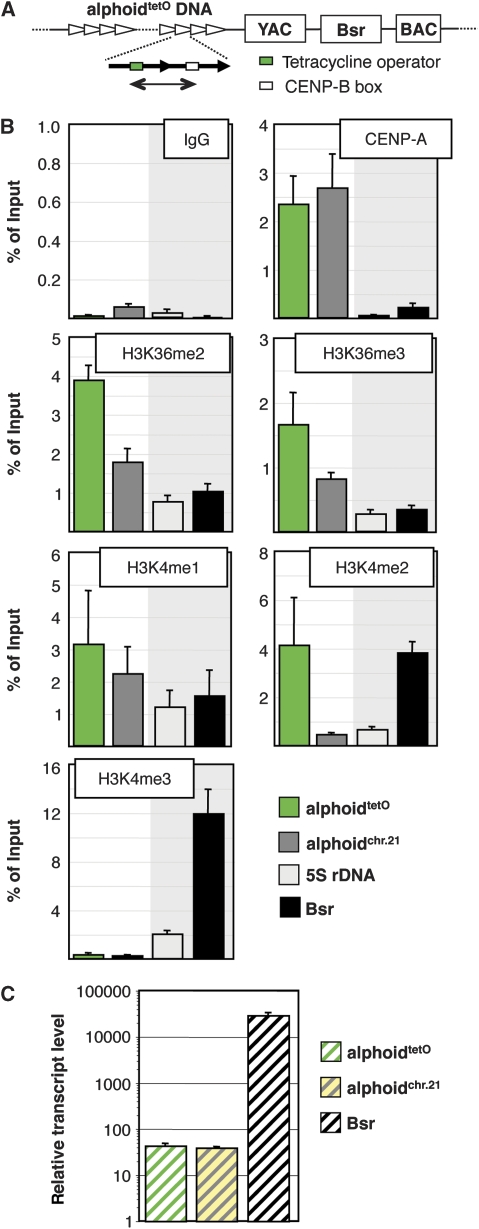
Figure 1.
Active centromere chromatin displays the signature of elongating RNA polymerase. (A) Schematic of the HAC, derived from Nakano et al (2008), indicating the synthetic alphoidtetO array (green: tetO; white: CENP-B box) and the HAC vector with YAC and BAC cassettes and the blasticidin (Bsr) resistance marker. The region of the alphoidtetO array analysed by ChIP is indicated by green line. (B) ChIP analysis in AB2.2.18.21 cells using antibodies of the indicated reactivity. The synthetic (alphoidtetO) centromere, endogenous chromosome 21 α21-I satellite DNA (alphoidchr.21), the 5S rDNA loci and the Bsr gene on the HAC vector were assessed. Data represent the mean and s.d. of three independent ChIP experiments. Note the different scaling of individual panels reflecting different efficiencies of individual antibodies. (C) Real-time RT–PCR analysis of synthetic HAC centromere (alphoidtetO), actively transcribed Bsr marker and endogenous chromosome 21 satellite (alphoidchr.21). Expression data are normalized to the copy number of the genomic regions and β-actin mRNA levels (see Materials and methods) and displayed as arbitrary numbers. Data represent the mean and s.e.m. of three independent experiments. Note the log scale.