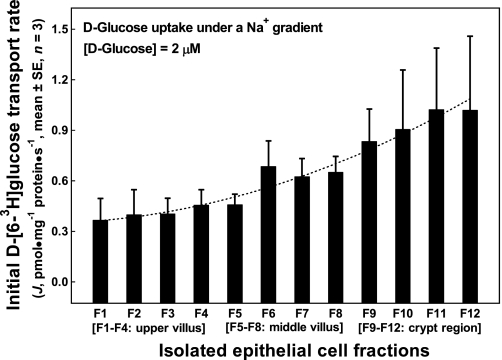
Fig. 1.
Initial rates of d-glucose uptake under a Na+ gradient into the apical membrane vesicles prepared from epithelial cells isolated along the jejunal crypt-villus axis in the liquid formula-fed neonatal pigs. Apical membrane vesicles were preloaded with a buffer containing 180 mM d-mannitol, 150 mM KSCN, 10 mM Trizma·HCl at pH 7.4. Uptake buffer contained 2.4 μM d-[6-3H]glucose, 180 mM d-mannitol, 150 mM NaSCN, and 10 mM Trizma·HCl at pH 7.4. The uptake media (60 μl), resulting from mixing 50 μl uptake buffer with 10 μl apical membrane vesicles, contained 2.0 μM d-[6-3H]glucose, 180 mM d-mannitol, 125 mM NaSCN, 25 mM KSCN, and 10 mM Trizma·HCl. Each point represents mean and SE (n = 3) of measurements from 3 uptake experiments (duplicate observations in each experiment) using 3 separate batches of apical membrane vesicle suspension prepared from 12 epithelial cell fractions (F1 through F12). Each batch of epithelial cell fractions was collected and pooled from the proximal and the distal jejunal segments of 2 piglets; thus a total of 6 piglets were used in these uptake experiments. J, rate of d-[6-3H]glucose tracer uptake into apical membrane vesicles.