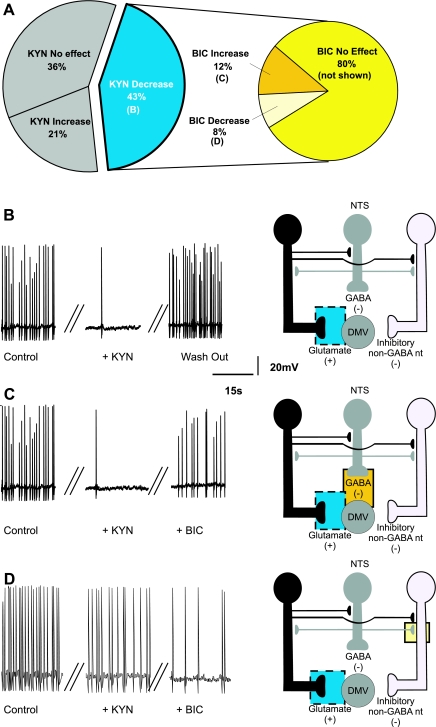
Fig. 5.
Pie charts (A), representative traces (B–D, left), and the proposed neuronal circuits (B–D, right) in neurons in which perfusion with KYN decreased the firing rate of DMV neurons. A: perfusion with KYN decreased (or abolished) the firing frequency of DMV neurons (N = 25), and BIC had no additional effect on the firing frequency in majority of these neurons. B: the decrease in firing rate induced by KYN is likely due to antagonism of glutamatergic receptors located on the membrane of the DMV neuron. C: perfusion with BIC in the presence of KYN increased the firing rate of DMV neurons (N = 3). This response was likely due to BIC-mediated inhibition of a tonic GABAergic input onto DMV neurons. D: perfusion with BIC in the presence of KYN further decreased the firing rate of DMV neurons (N = 2), suggesting the presence of tonic GABAergic synapses impinging onto non-GABAergic neurons.