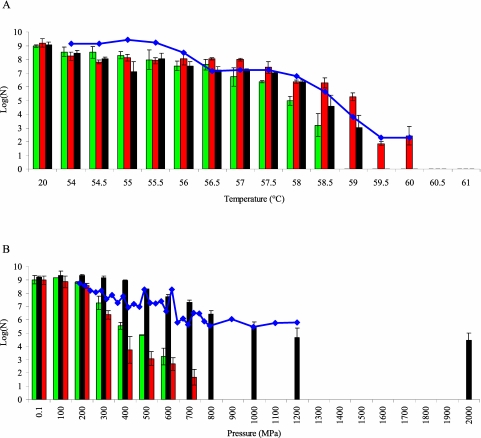
FIG 1 .
Directed evolution of E. coli K-12 MG1655 towards heat (at atmospheric pressure) (A) or HP (at ambient temperature) (B) resistance. An axenic culture of E. coli MG1655 was iteratively exposed to progressively intensifying temperature or pressure shocks (15 min each), with a resuscitation and growth step between consecutive treatments. Survival after each treatment was determined (blue diamonds) and expressed as log(N), in which N represents the number of survivors determined by plate counts and expressed as CFU per milliliter. At the end of both selection regimens, the most heat (red bars)- and pressure (black bars)-resistant clone that had enriched in the respective cultures was isolated and its acquired heat (A) and HP (B) resistance was determined and compared to that of the original parental strain (green bars). It should be noted that these selection profiles are representative of 20 and 4 independent trials for heat and HP resistance development, respectively. Further experimental details can be found in the supplemental material (Text S1).