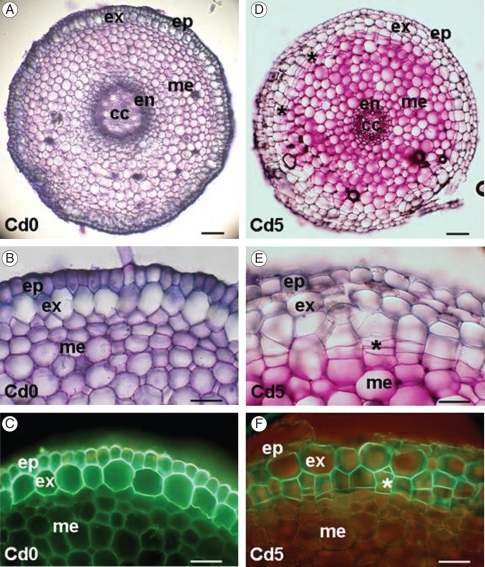
Fig. 7.
Cross-sections of adventitious roots of Merwilla plumbea. Plants were grown in control conditions in perlite (A–C) and treated with 5 mg kg−1 Cd (D–F). Roots in control conditions exhibit the typical structure of monocotyledonous roots formed by single-layered epidermis and single-layered exodermis (A, B); exodermal cells develop suberin lamellae close to the root apex, as shown in C after Fluorol yellow 088 staining in fluorescence microscopy. After cadmium treatment the hypodermal periderm is formed in the peripheral cortical zone close to the root apex (D–F). Cork cambium produces cells by periclinal division (E); these become impregnated by suberin, as shown in F after Fluorol yellow 088 staining in fluorescence microscopy. The distances of sections from the root apex are 5 mm (A, B, D, E) and 30 mm (C, F). Abbreviations: ep, epidermis; ex, exodermis; me, mesodermis (mid-cortical layers); en, endodermis; cc, central cylinder; asterisks indicate periclinal divisions in cork cambium. Scale bars: (A, D) = 100 µm, (B, C, E, F) = 50 µm.