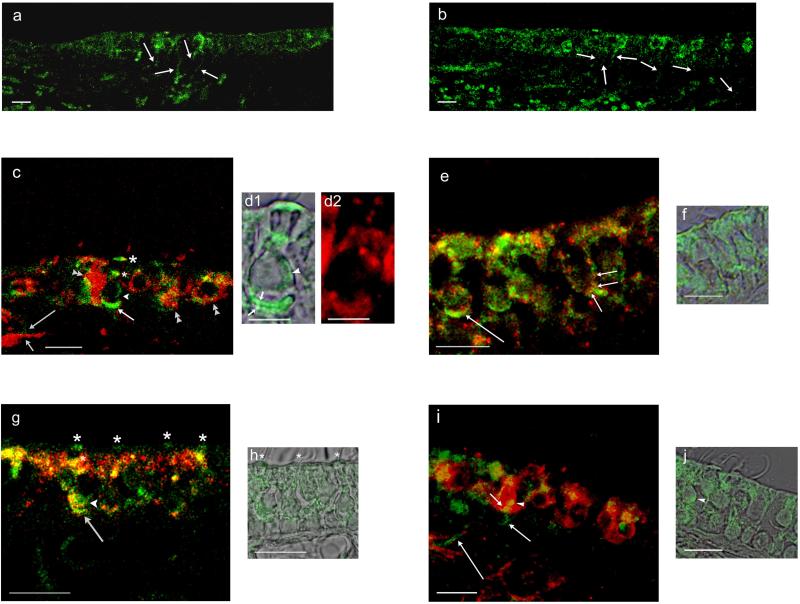
Fig. 10. Dopamine D1 and D2L and tyrosine hydroxylase immunofluorescence in the rat saccule and utricle in comparison with calyceal afferent marker calretinin and AC5/6.
a. Dopamine D1A-positive nerve fibers passed from the connective tissue through the basal lamina to the saccular sensory epithelium of the rat saccule (arrows). b. Dopamine D2L immunofluorescence was localized to nerve fibers which traveled from the connective tissue through the basal lamina to the sensory epithelium of rat saccule (arrows). c. Dopamine D1A immunofluorescence (green) was compared with immunofluorescence for calretinin (red). D1A-positive nerve fibers (long arrow) shadow the calretinin-positive fibers (short arrow) within the connective tissue before passing into the sensory epithelium. Within the sensory epithelium, overlap of dopamine D1A and calretinin immunoreactivity (merge, yellow) occurred on calretinin-containing calyces (double arrowheads) and on calyces at the base of type I vestibular hair cells (intermediate-length arrow). D1A immunoreactivity was found on the cell membrane of the type 1 vestibular hair cell (arrowhead) and at two supranuclear sites (asterisks), one close to the reticular lamina (larger asterisk). d1. D1A immunoreactivity and overlapping differential interference contrast (DIC) image of a type I vestibular hair cell illustrated in c, with immunoreactivity on both faces of the calcyceal afferent (short arrows), on basolateral aspects of the hair cell membrane (arrowhead), and at both intermediate and apical (subcuticular) supranuclear sites. d2. Calretinin immunoreactivity for calyx surrounding the type I vestibular hair cell depicted in d1. e. Dopamine D1 and AC5/6 in rat utricle. AC5 immunofluorescence (green) overlapped/co-localized with dopamine D1 immunofluorescence (red) at a calyceal ending on type I vestibular hair cell (long arrow) (merge, yellow). Co-localization of AC5/6 with dopamine D1 was observed on the basal cell membrane of a type II vestibular hair cell (short arrows) close to a putative efferent nerve ending. f. AC5/6 immunofluorescence image of vestibular type II hair cell illustrated in e overlapping DIC images in adjacent section. g. Dopamine D2L and AC5/6 in rat saccule. Dopamine D2L immunofluorescence (green) co-localized with AC5/6 immunofluorescence (red) at calyceal afferent endings on type I vestibular hair cells (arrow), at the base of type I vestibular hair cell (arrowhead) and at supranuclear sites (asterisks) (merge, yellow). h. DIC and D2L immunoreactivity for the same section. Positions of D2L immunofluorescence at subcuticular sites are marked by asterisks corresponding to first three asterisks in g (left to right). i. Immunofluorescence (green) for tyrosine hydroxylase, a dopaminergic/catecholaminergic (efferent) neuronal marker, was compared to immunofluorescence (red) for calretinin, a calyceal afferent marker. The merged image indicates a small-diameter, tyrosine-positive fiber (green, intermediate-length arrow) in the connective tissue passing through the basal lamina into the sensory epithelium to end (short arrow) on a calyceal afferent (red) of a type I vestibular hair cell (overlap/co-localization in yellow). Tyrosine hydroxylase-positive nerve fibers (presumptive efferents) passed through the connective tissue en route to the sensory epithelium (long arrows). j. DIC and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in same section with arrowhead pointing to same site of accumulation of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity on cell body of a type I vestibular hair cell in i and j. Scale bars = 10 μm, except for d (5 μm).