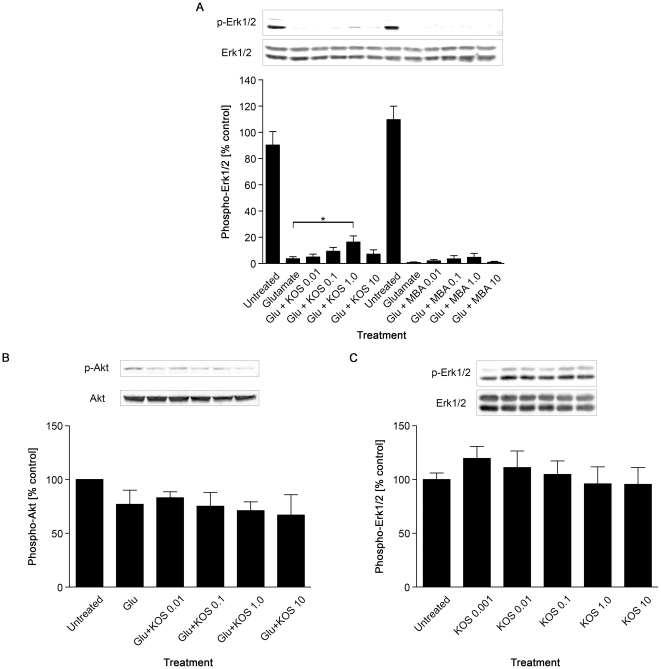
Figure 1. Koshu GSE alleviates glutamate-induced inactivation of Erk1/2 in cultured hippocampal neurons.
(A) Top, detection of phosphorylated Erk1/2 in cultured hippocampal neurons by western blot. Neurons were treated with 50 µM glutamate alone or in the presence of indicated concentrations (in ng/ml) of KOS or MBA for 30 min. The immunoblot for total Erk1/2 shows equal loading. Bottom, quantification of phospho-Erk1/2 levels by image analysis (n = 5). The relative values to the untreated controls (set to 100%) are shown. *, P<0.05 versus untreated controls. (B) Hippocampal neurons were treated with 50 µM glutamate with or without indicated concentrations (in ng/ml) of KOS GSE for 30 min, and 200 µg of total protein were loaded in each lane for western blot analyses for phospho- and total Akt. The basal Akt phosphorylation appeared slightly diminished upon glutamate insult. KOS GSE did not show any protective effect on basal Akt phosphorylation levels. (C) The effect of KOS GSE alone on Erk1/2 phosphorylation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Cells were treated with indicated concentrations (in ng/ml) of KOS GSE for 30 min. Top, representative western blot images of phospho- and total-Erk1/2. Bottom, a quantification of the phospho-Erk1/2 levels by image analysis (n = 3).