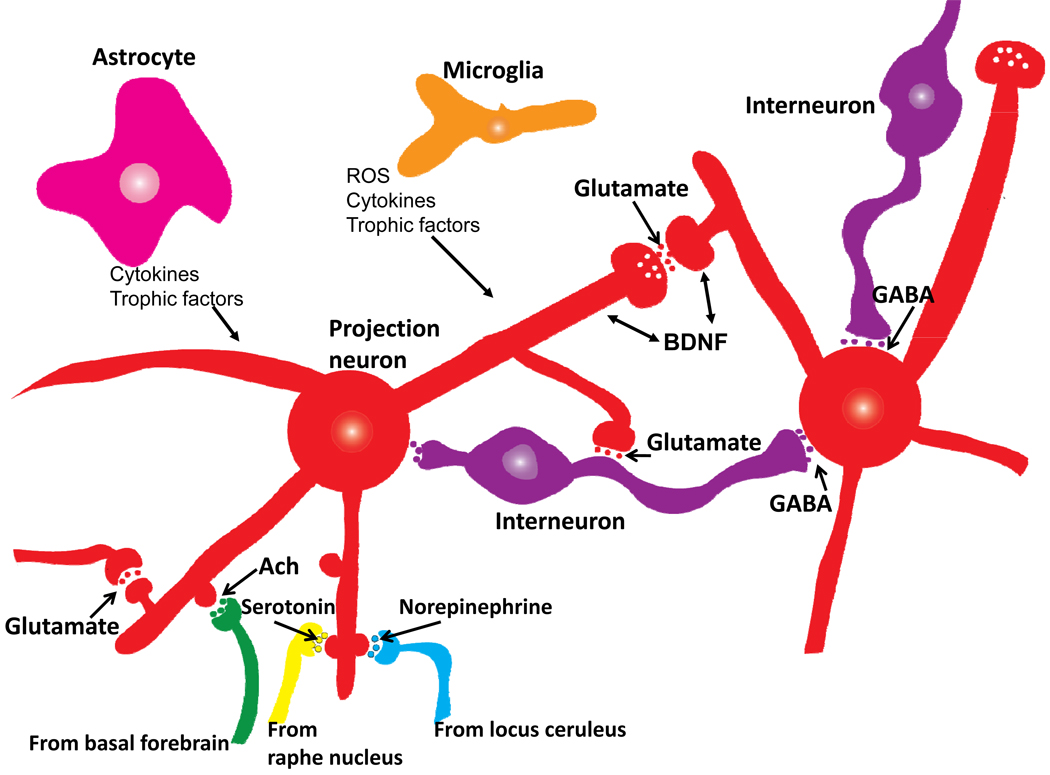
Figure 3.
Basic organization of neuronal microcircuits that control information flow through all brain regions involved in cognitive processing. The major excitatory projection neurons are glutamatergic with long axons that synapse on dendrites of other glutamatergic neurons that may, in turn, project their axons to a different brain region. GABAergic interneurons receive excitatory inputs from glutamatergic neurons and form synapses on the cell bodies of the same or other glutamatergic neurons. Glutamatergic neurons also receive synaptic inputs from noradrenergic, serotonergic and cholinergic neurons whose cell bodies are located in the locus ceruleus, raphe nucleus and basal forebrain, respectively. Neurons in all brain regions also interact with glial cells including astrocytes and microglia which produce trophic factors and cytokines which may normally play important roles in synaptic plasticity. However, excessive production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species (ROS) by glial cells has been implicated in the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment and AD.