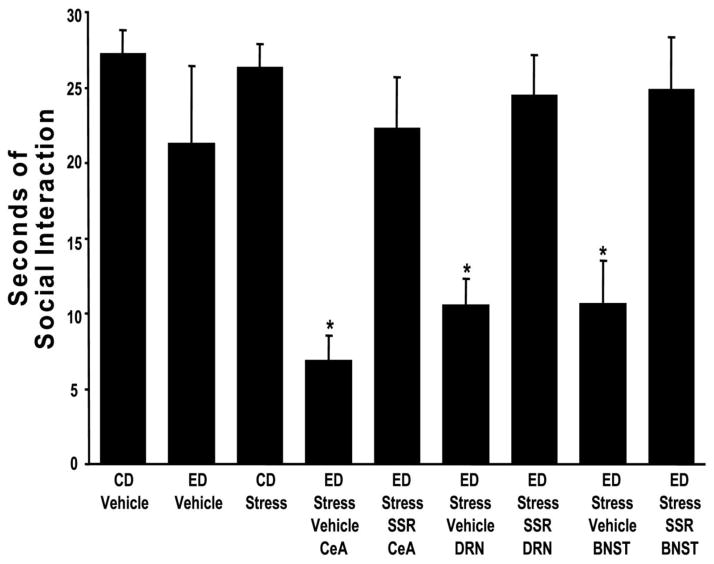
Figure 7. Microinjection of a CRF1-R antagonist (SSR) into the CeA, DRN, or dBNST prior to restraint stress prevents sensitization of alcohol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior (reduction in social interaction).
The CRF-1 receptor antagonist SSR125543 (SSR; 10 μg/0.5 μl) was microinjected into the CeA, DRN, or the dorsal BNST (BNST) 15 min prior to the 2 weekly 60-min restraint stresses applied before exposure to 5 days of 4.5% alcohol diet (ED). For the CD-Vehicle and ED-Vehicle groups, vehicle was administered into each of the brain sites (N = 3–6 for each site) and these data combined. Social interaction, as a measure of anxiety-like behavior, was determined 5–6 hrs after alcohol removal. The CD-Vehicle group was not significantly different from the ED-vehicle group. *P < 0.001 when compared to the CD-Vehicle, ED-Vehicle, and CD Stress groups as well as the groups that received the CRF1R antagonist (SSR) into the three brain sites prior to the repeated stresses. From Huang et al. (2009) by permission of the publisher.