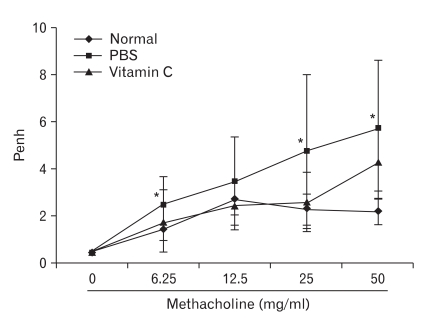
Fig. 1.
Plethysmography of normal and asthma-induced mice. Mice were inhaled with aerosol containing methacholine at concentrations indicated and placed in the plethymography chamber. Breathing was recorded for 2 min and airway resistance was calculated thereby. PBS-treated mice with asthma (■) showed increased airway resistance compared to normal mice (◆) at all concentrations of methacholine. Meanwhile, vitamin C-treated mice with asthma (▲) showed decreased resistance than that of PBS-injected mice, and that was similar to that of normal mice at methacholline concentrations from 6.25 to 25 mg/ml. *P<0.05.