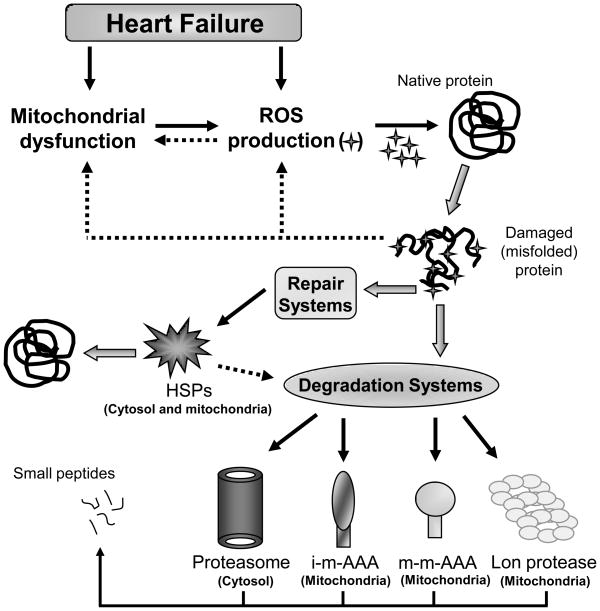
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the protease and chaperone systems involved in mitochondrial protein quality control.
Oxidation by reactive oxygen species damages mitochondrial proteins in either reversible or irreversible manners, and accumulation of oxidized/damaged proteins can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction in heart failure. Intracellular elimination of oxidatively modified proteins is achieved in the mitochondria and cytosol by either degradation (Lon, proteasome and m-AAA proteases) or specific repair systems (HSPs-heat shock proteins).